Quantum States in a Nano-object Manipulated using a Mechanical System
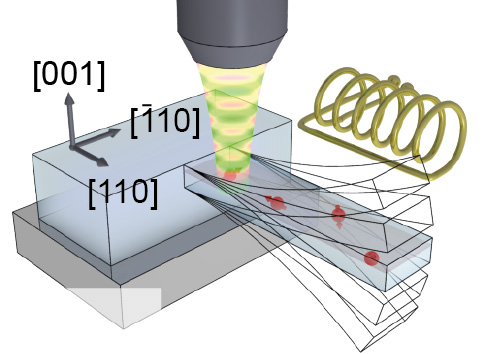
The oscillating resonator influences the electron spin in the nitrogen-vacancy centers (red arrows). Their spin can be efficiently read out by fluorescence microscopy. University of Basel
In previous publications, the research team led by Georg H. Endress Professor Patrick Maletinsky described how resonators made from single-crystalline diamonds with individually embedded electrons are highly suited to addressing the spin of these electrons.
These diamond resonators were modified in multiple instances so that a carbon atom from the diamond lattice was replaced with a nitrogen atom in their crystal lattices with a missing atom directly adjacent. In these “nitrogen-vacancy centers,” individual electrons are trapped. Their “spin” or intrinsic angular momentum is examined in this research.
When the resonator now begins to oscillate, strain develops in the diamond’s crystal structure. This, in turn, influences the spin of the electrons, which can indicate two possible directions (“up” or “down”) when measured. The direction of the spin can be detected with the aid of fluorescence spectroscopy.
Extremely fast spin oscillation
In this latest publication, the scientists have shaken the resonators in a way that allows them to induce a coherent oscillation of the coupled spin for the first time. This means that the spin of the electrons switches from up to down and vice versa in a controlled and rapid rhythm and that the scientists can control the spin status at any time. This spin oscillation is fast compared with the frequency of the resonator. It also protects the spin against harmful decoherence mechanisms.
It is conceivable that this diamond resonator could be applied to sensors – potentially in a highly sensitive way – because the oscillation of the resonator can be recorded via the altered spin.
These new findings also allow the spin to be coherently rotated over a very long period of close to 100 microseconds, making the measurement more precise. Nitrogen-vacancy centers could potentially also be used to develop a quantum computer. In this case, the quick manipulation of its quantum states demonstrated in this work would be a decisive advantage.
Original source
Arne Barfuss, Jean Teissier, Elke Neu, Andreas Nunnenkamp, Patrick Maletinsky
Strong mechanical driving of a single electron spin
Nature Physics (2015), doi: 10.1038/nphys3411
Further information
Professor Patrick Maletinsky, University of Basel / Swiss Nanoscience Institute, tel. +41 61 267 37 63, email: patrick.maletinsky@unibas.ch
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nphys3411 – Abstract
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.unibas.chAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

A ‘language’ for ML models to predict nanopore properties
A large number of 2D materials like graphene can have nanopores – small holes formed by missing atoms through which foreign substances can pass. The properties of these nanopores dictate many…

Clinically validated, wearable ultrasound patch
… for continuous blood pressure monitoring. A team of researchers at the University of California San Diego has developed a new and improved wearable ultrasound patch for continuous and noninvasive…

A new puzzle piece for string theory research
Dr. Ksenia Fedosova from the Cluster of Excellence Mathematics Münster, along with an international research team, has proven a conjecture in string theory that physicists had proposed regarding certain equations….



