Math Boosts Brain Research
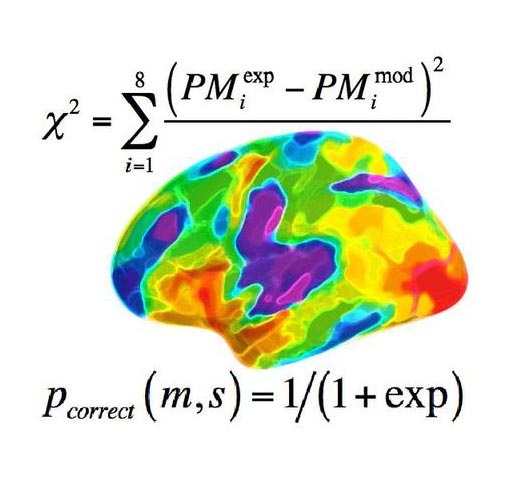
Researchers at the University of Basel succeeded at describing distinct memory processes, such as learning, remembering and forgetting using a computational model. (Fig: MCN University of Basel)
Thanks to our memory we are able to learn foreign languages, solve exams and remember beautiful moments from the past. To ensure optimal memory performance, several distinct cognitive processes have to cooperate. Information is first learned and then stored. Later, when we want to remember them, we depend on a properly functioning retrieval process.
If all these various memory processes are controlled by the same or by different genes and molecular mechanisms has so far been mostly unknown. One reason for this, is the fact that many of these processes are not amenable to direct measurement and have therefore remained inaccessible for science.
The mathematician Dr. Gediminas Luksys from the transfaculty research platform at the Psychiatric University Clinics Basel and the Faculty of Psychology at the University of Basel has now been able to successfully describe the various human memory processes for the first time. The study used data of over 1700 adults. Thanks to the computational model, the researchers were able to measure the processes and to conduct distinct genetic analyses for the specific mental processes.
Individual processes are based on different gene sets
The results show that distinct genetic profiles underlie specific memory processes: The study reports, for example, associations between a transporter protein set and the process of learning as well as between a cell adhesion set and the process of memory storage. The findings contribute to a better understanding of the complex processes of human memory and could lead to the development of new treatment therapies for various memory disorders in the future.
The current study is part of the Basel Genetics Memory Project led by Prof. Dominique de Quervain and Prof. Andreas Papassotiropoulos. The two co-heads of the transfaculty research platform are dedicated to getting these fundamental research results transfered to therapy projects as fast as possible.
Original source
Gediminas Luksys, Matthias Fastenrath, David Coynel, Virginie Freytag, Leo Gschwind, Angela Heck, Frank Jessen, Wolfgang Maier, Annette Milnik, Steffi G. Riedel-Heller, Martin Scherer, Klara Spalek, Christian Vogler, Michael Wagner, Steffen Wolfsgruber, Andreas Papassotiropoulos, and Dominique J.-F. de Quervain
Computational dissection of human episodic memory reveals mental process-specific genetic profiles
PNAS (2015), doi: 10.1073/pnas.1500860112
Further information:
Prof. Dr. Dominique de Quervain, University of Basel, Transfaculty Research Platform Molecular and Cognitive Neurosciences, tel. +41 61 267 02 37, email: dominique.dequervain@unibas.ch
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.unibas.chAll latest news from the category: Studies and Analyses
innovations-report maintains a wealth of in-depth studies and analyses from a variety of subject areas including business and finance, medicine and pharmacology, ecology and the environment, energy, communications and media, transportation, work, family and leisure.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



