NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP sees a lopsided Tropical Storm Henri
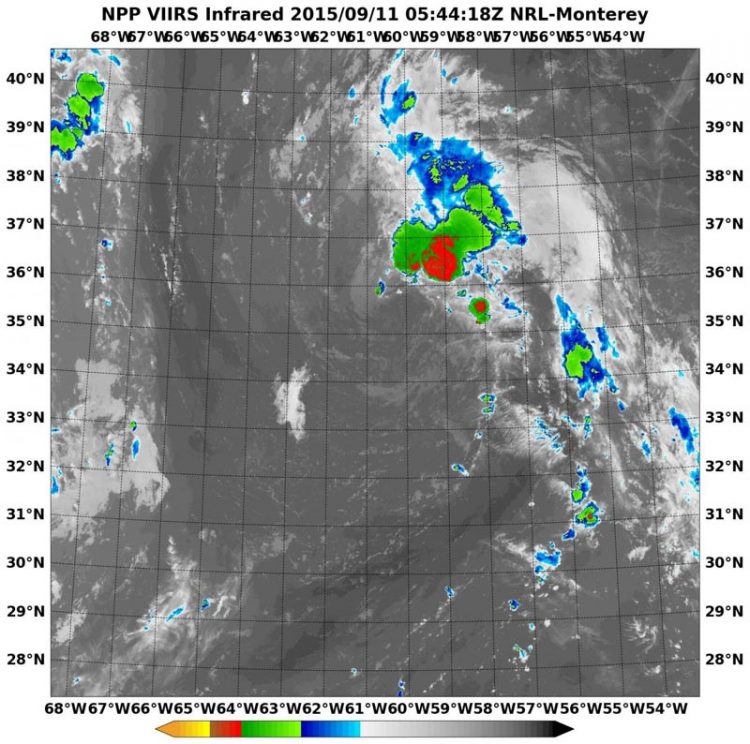
NASA-NOAA's Suomi satellite flew over Henri at 5:44 UTC (1:44 a.m. EDT) on Sept. 11 and the VIIRS instrument aboard captured this infrared image that showed most of the thunderstorms northeast of the center. Credits: NRL/NASA/NOAA
At 0544 UTC (1:44 a.m. EDT) Infrared data from the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite or VIIRS instrument that flies aboard Suomi NPP showed cloud top temperatures in the northeastern quadrant of Henri were as cold as -63F/-53C, indicating strong storms reaching high into the troposphere. Clouds around the rest of the tropical storm were warmer (and much lower in the atmosphere) and devoid of rainfall.
Southeasterly wind shear is responsible for pushing the clouds and showers to the northeast of Henri's center. In addition, there's dry air around the system which is inhibiting the development of thunderstorms in the other areas of the storm.
National Hurricane Center forecaster Kimberlain noted on September 11 at 5 a.m. EDT, “While nearly all of the cyclone's deep convection is still located well to the northeast of the center, a relatively new convective burst over this area has grown in coverage and cloud tops have cooled.”
At 5 a.m. EDT (0900 UTC), the center of Tropical Storm Henri was located near latitude 36.2 North, longitude 60.3 West. That's about 370 miles (600 km) northeast of Bermuda and about 815 miles (1,310 km) south-southwest of Cape Race Newfoundland, Canada.
Maximum sustained winds were near 40 mph (65 kph) and little change in strength is forecast during the next two days. However, Henri is expected to become a post-tropical storm by September 13.
Henri is moving toward the north near 16 mph (26 kph) and the National Hurricane Center forecast calls for a turn toward the north-northeast then to the northeast by Sunday, September 13.
The NHC noted that the southerly vertical shear appears to be diminishing over the cyclone so some additional intensification could occur later on September 11.
However, forecaster Kimberlain noted “the continued presence of dry air in the near-storm environment and Henri's disorganized appearance suggest that any intensification should be negligible. After the cyclone crosses the northern wall of the Gulf Stream in less than 18 hours, substantially lower sea surface temperatures and increasingly stable air should induce weakening soon after that.” For updated forecasts, visit the NHC website: http://www.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



