Olympus Mons – the caldera in close-up
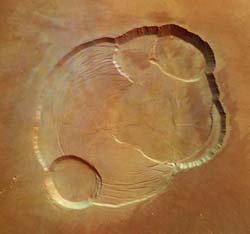
Complex caldera of Olympus Mons - Mars Express
View from overhead of the the complex caldera (summit crater) at the summit of Olympus Mons on Mars, the highest volcano in our Solar System.
Olympus Mons has an average elevation of 22 km and the caldera has a depth of about 3 km. This is the first high-resolution colour image of the complete caldera of Olympus Mons.
The image was taken from a height of 273 km during orbit 37 by the High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) on ESA’s Mars Express on 21 January 2004. The view is centred at 18.3°N and 227°E. The image is about 102 km across with a resolution of 12 m per pixel. South is at the top.
This complementary 3D view shows the Olympus Mons volcano in its entirety, to put the caldera images in context. It has been derived from the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) topographic data superimposed with the Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) wide-angle image mosaic.
This perspective view shows the southern part of the caldera. The image has been calculated from the digital elevation model derived from the stereo channels and combined with the nadir- and colour-channels of the Mars Express HRSC.
The scene reveals tongue-shaped mass-movement features in 3D on the southern wall. The striations are tectonic faults. After lava production has ceased the caldera collapsed over the emptied magma chamber. Through the collapse the surface suffers from extension and thus, extensional fractures are formed. The elevation level on which these fractures can be observed represents the event of the oldest caldera collapse. Later lava production has produced new caldera collapses at different locations (the other circular depressions), they partly destroyed the cicular fracture pattern of the oldest one.
The data has been retrieved from a height of 273 km during orbit 37 on 21 January 2004. The view is centred at 18.3°N and 227°E. The image is about 40 km across. The vertical exaggeration is 1.8. South is up to allow the mass-movement features to be seen.
This perspective view has been calculated from the digital elevation model derived from the stereo channels and combined with the nadir- and colour- channels of the HRSC.
The data has been retrieved from a height of 273 km in orbit 37 on 21 January 2004. The view is centred at 18.3°N and 227°E. The image is 102 km across and has a resolution of 12 m per pixel. The vertical exaggeration is 1.8. South is up.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.esa.int/export/SPECIALS/Mars_Express/SEM9BA1PGQD_0.htmlAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…


