Physicists mimic quantum entanglement with laser pointer to double data speeds
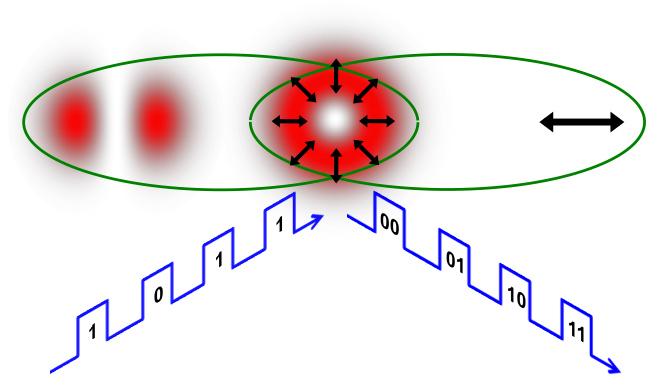
The shape and polarization of a conventional laser beam from a laser pointer mimics quantum entanglement when the laser beam has a polarization dependent shape. This can be used to encode twice as many bits of information as when the laser beam is "separable." Credit: Giovanni Milione
Quantum entanglement is a phrase more likely to be heard on popular sci-fi television shows such as “Fringe” and “Doctor Who.” Described by Albert Einstein as “spooky action at a distance,” when two quantum things are entangled, if one is 'touched' the other will 'feel it,' even if separated by a great distance.
“At the heart of quantum entanglement is 'nonseparability' – two entangled things are described by an unfactorizable equation,” said City College PhD student Giovanni Milione. “Interestingly, a conventional laser beam (a laser pointer)'s shape and polarization can also be nonseparable.”
To make the laser beam's shape and polarization nonseparable, the researchers transformed it into what Milione refers to as a vector beam – a polarization dependent shape. Then using off-the-shelf components to 'touch' only its polarization, they showed it could be encoded as two bits of information.
Surprisingly, this was twice as much information that could be encoded as when the laser beam was separable.
“In principal, this could be used to double the data speed of laser communication,” said CCNY Distinguished Professor of Phyiscs Robert Alfano. “”While there's no 'spooky action at a distance,' it's amazing that quantum entanglement aspects can be mimicked by something that simple.”
An article on the experiment appears in the latest issue of the journal “Optics Letters” and was supported in part by the Army Research Office.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



