Master switch for brain development
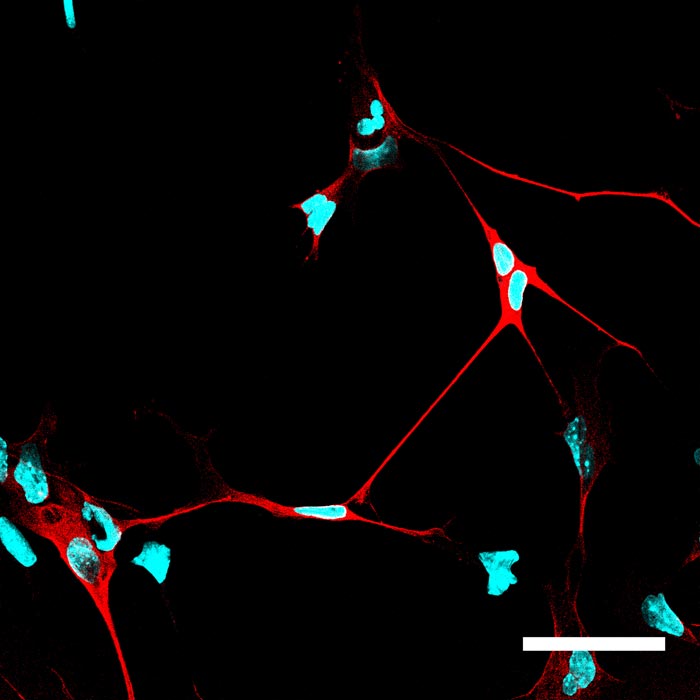
Cells in which NeuroD1 is turned on are reprogrammed to become neurons. Cell nuclei are shown in blue (Höchst stain) and neurons, with their characteristic long processes, are shown in red (stained with neuronal marker TUJ1). Credits: A. Pataskar/J. Jung & V. Tiwari
Neurodegenerative disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, are often characterized by an irreversible loss of brain cells. Unlike many other cell types in the body, these neurons are generally not able to regenerate by themselves, so if the brain is damaged, it stays damaged.
One hope of developing treatments for this kind of damage is to understand how the brain develops in the first place, and then try to imitate the process. However, the brain is also one of the most complex organs in the body, and very little is understood about the molecular pathways that guide its development.
Scientists in Dr. Vijay Tiwari's group at the Institute of Molecular Biology at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz have been investigating a central gene in brain development, NeuroD1. This gene is expressed in the developing brain and marks the onset of neurogenesis.
In their research article, Tiwari and his colleagues have shown that during brain development NeuroD1 is not only expressed in brain stem cells but acts as a master regulator of a large number of genes that cause these cells to develop into neurons.
They used a combination of neurobiology, epigenetics, and computational biology approaches to show that these genes are normally turned off in development, but NeuroD1 activity changes their epigenetic state in order to turn them on. Strikingly, the researchers show that these genes remain switched on even after NeuroD1 is later switched off.
They further show that this is because NeuroD1 activity leaves permanent epigenetic marks on these genes that keep them turned on, in other words it creates an epigenetic memory of neuronal differentiation in the cell.
Abhijeet Pataskar and Johannes Jung, joint first authors on the paper, explained the significance of this discovery: “Our research has shown how a single factor, NeuroD1, has the capacity to change the epigenetic landscape of the cell, resulting in a gene expression program that directs the generation of neurons.”
Dr. Vijay Tiwari is excited about the implications of these findings: “This is a significant step towards understanding the relationship between DNA sequence, epigenetic changes, and cell fate. It not only sheds new light on the formation of the brain during embryonic development but also opens up novel avenues for regenerative therapy.”
PUBLICATIONS
Pataskar A*, Jung J*, Smialowski P, Noack F, Calegari F, Straub T and Tiwari VK (2015). NeuroD1 reprograms chromatin and transcription factor landscapes to induce the neuronal program. EMBO J, pii: e201591206. [Epub ahead of print]. (*indicates equal contribution)
News & Views by Glahs A, Zinzen RP (2015). Putting chromatin in its place: the pioneer factor NeuroD1 modulates chromatin state to drive cell fate decisions. EMBO J, Nov 13, DOI: 10.15252/embj.201593324
Further information about Dr. Vijay Tiwari’s research can be found at http://www.imb.de/tiwari.
About the Institute of Molecular Biology gGmbH
The Institute of Molecular Biology gGmbH (IMB) is a center of excellence in the life sciences that was established in 2011 on the campus of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU). Research at IMB concentrates on three cutting-edge areas: epigenetics, developmental biology, and genome stability. The institute is a prime example of a successful collaboration between public authorities and a private foundation. The Boehringer Ingelheim Foundation has dedicated EUR 100 million for a period of ten years to cover the operating costs for research at IMB, while the state of Rhineland-Palatinate provided approximately EUR 50 million for the construction of a state-of-the-art building.
About the Boehringer Ingelheim Foundation
The Boehringer Ingelheim Foundation is an independent, non-profit organization committed to the promotion of the medical, biological, chemical, and pharmaceutical sciences. It was established in 1977 by Hubertus Liebrecht (1931-1991), a member of the shareholder family of the company Boehringer Ingelheim. With the PLUS 3 Perspectives Program and the Exploration Grants, the foundation supports independent group leaders. It also endows the internationally renowned Heinrich Wieland Prize as well as awards for up-and-coming scientists. In addition, the foundation pledged to donate EUR 100 million to finance the scientific running of the IMB at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz for ten years. In 2013, the Boehringer Ingelheim Foundation donated a further EUR 50 million to Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz.
http://www.imb.de – Institute of Molecular Biology (IMB)
http://www.imb.de/tiwari – Dr. Vijay Tiwari's research at IMB
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



