New supercomputer simulations enhance understanding of protein motion and function
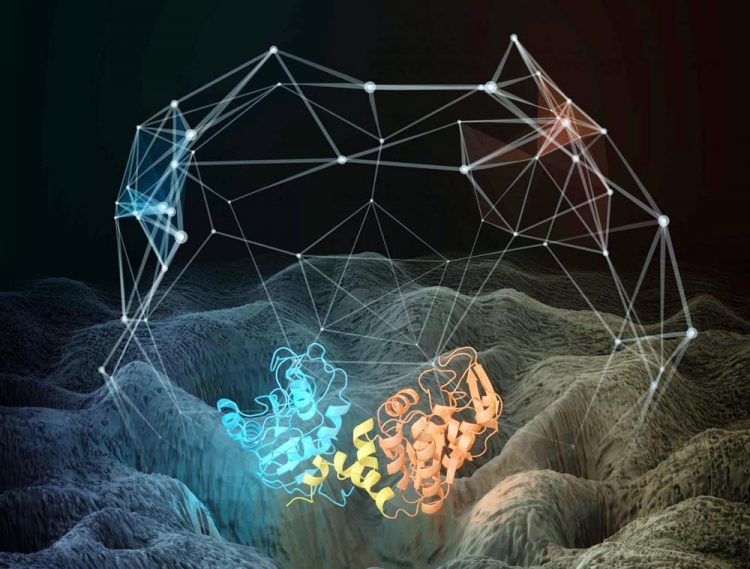
This is an illustration of the structure of a phosphoglycerate kinase protein that was subjected to molecular dynamics simulations. The relative motions of the red and blue domains of the proteins are highly complex, and can be described in terms of motion of a configurational point on a rough energy landscape (illustrated). The transitions of the structure between energy minima on the landscape can be described in terms of a network (illustrated), which is found to be fractal (self-similar) on every timescale. Credit: Thomas Splettstoesser; http://www.scistyle.com
“Proteins have never been seen this way before,” said coauthor Jeremy Smith, director of ORNL's Center for Molecular Biophysics and a Governor's Chair at the University of Tennessee (UT). “We used considerable computer power to provide a unified conceptual picture of the motions in proteins over a huge range of timescales, from the very shortest lengths of time at which atoms move (picoseconds) right up to the lifetimes of proteins in cells (roughly 1000 seconds). It changes what we think a protein fundamentally is.”
Studying proteins–their structure and function–is essential to advancing understanding of biological systems relevant to different energy and medical sciences, from bioenergy research and subsurface biogeochemistry to drug design.
Results obtained by Smith's UT graduate student, Xiaohu Hu, revealed that the dynamics of single protein molecules are “self-similar” and out of equilibrium over an enormous range of timescales.
With the help of Titan– the fastest supercomputer in the U.S., located at the DOE Office of Science's Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility–Smith's team developed a complete picture of protein dynamics, revealing that the structural fluctuations within any two identical protein molecules, even if coded from the same gene, turn out to be different.
“A gene is a code for a protein, producing different copies of the protein that should be the same, but the internal fluctuations of these individual protein molecules may never reach equilibrium, or converge,” Smith said. “This is because the fluctuations themselves are continually aging and don't have enough time to settle down before the protein molecules are eaten up in the cell and replaced.”
Understanding the out-of-equilibrium phenomenon has biological implications because the function of a protein depends on its motions. Two individual protein molecules, even though they come from the same gene, will not function precisely the same way within the cell.
“You may have, for example, two identical enzyme molecules that catalyze the same reaction,” said Smith. “But due to the absence of equilibrium, the rate at which the catalysis happens will be slightly different for the two proteins. This affects the biological function of the protein.”
The team also discovered that the dynamics of single protein molecules are self-similar, or fractal over the whole range of timescales. In other words, the motions in a single protein molecule look the same however long you look at them for, from picoseconds to hundreds of seconds.
“The motions in a protein, how the bits of the protein wiggle and jiggle relative to each other, resemble one another on all these timescales,” Smith said. “We represent the shape of a protein as a point. If it changes its shape due to motions, it goes to a different point, and so on. We joined these points, drawing pictures, and we found that these pictures are the same when you look at them on whatever timescale, whether it's nanoseconds, microseconds, or milliseconds.”
By building a more complete picture of protein dynamics, the team's research reveals that motions of a single protein molecule on very fast timescales resemble those that govern the protein's function.
To complete all of the simulations, the team combined the power of Titan with two other supercomputers–Anton, a specialty parallel computer built by D.E. Shaw Research, and Hopper, the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center's Cray XE6 supercomputer located at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
“Titan was especially useful for us to get accurate statistics,” Smith said. “It allowed us to do a lot of simulations in order to reduce the errors and get more confident results.”
The title of the Nature Physics paper is “The Dynamics of Single Protein Molecules is Non-Equilibrium and Self-Similar Over Thirteen Decades in Time.”
This research was supported by the DOE Office of Science through an Advanced Scientific Computing Research (ASCR) Leadership Computing Challenge (ALCC) allocation and funded in part by a DOE Experimental Program to Stimulate Competitive Research (EPSCoR) award. The Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility and National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center are DOE Office of Science User Facilities.
ORNL is managed by UT-Battelle for the Department of Energy's Office of Science. DOE's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit http://science.
###
NOTE TO EDITORS: You may read other press releases from Oak Ridge National Laboratory or learn more about the lab at http://www.
Twitter – http://twitter.
RSS Feeds – http://www.
Flickr – http://www.
YouTube – http://www.
LinkedIn – http://www.
Facebook – http://www.
Media Contact
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



