Study heralds new chapter in infectious disease research
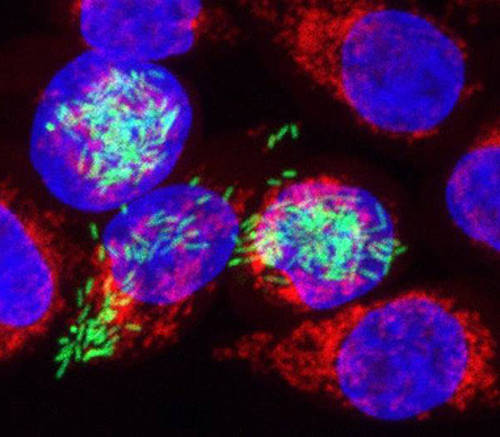
A new method developed at the University of Würzburg allows researchers to shed light on the details of what happens in pathogens and affected host cells during an infection. The image shows human cells (red/blue) infected with Salmonella (green). The bacteria were marked with a fluorescent dye. (Photo: IMIB)
The study led by Professor Jörg Vogel from the Würzburg Institute of Molecular Infection Biology also involved researchers from Leipzig and Cologne. The scientists investigated the initial events that occur during the first few hours following a Salmonella infection. These bacteria are a leading cause of food-borne illnesses and when ingested with contaminated food, they multiply in the intestine causing the symptoms associated with severe food poisoning.
There remains much to be learnt about how the pathogens affect the host cell and also how the infected cell responds to the presence of the bacteria. Researchers have now devised a new approach, called dual RNA sequencing, to study both these aspects. This method enables them to look at an important group of specific molecules, RNAs, in human cells infected with the pathogen Salmonella Typhimurium.
RNA is present in all living cells and serves many different functions. For instance, traditionally, RNA has been viewed as a messenger that transmits the genetic information from genes into proteins, however, recently many RNAs themselves have been shown to control important processes in the cell.
By isolating the entire RNA content from infected cells, i.e. the RNA from both bacteria and host, this allowed the scientists to describe in detail which of its approximately 5,000 genes Salmonella activates or deactivates during the different stages of infection. At the same time, they analysed how the more than 40,000 genes of the host cells respond to the pathogen.
Small molecule, huge impact
Their analysis revealed that Salmonella boosts the production of a bacterial RNA molecule named PinT by more than a hundred fold during an infection. PinT does not encode for a protein, but belongs to a special group of bacterial RNAs called small RNAs (sRNAs).
These sRNAs are relatively small RNA molecules that are responsible for fine-tuning gene activity: For example, they make sure that proteins are produced at the correct time by controlling the availability of messenger RNAs. There are many of these sRNAs in a bacterial cell but in the majority of cases their roles during an infection are largely unknown. “To understand what PinT does we generated a Salmonella mutant that is incapable of producing it,” Dr. Alexander Westermann from the Würzburg Institute for Molecular Infection Biology explains. “Then we looked at how this mutant behaves during an infection.”
The result was astonishing: The miniature molecule clearly affects a whole range of bacterial genes, in particular the virulence factors. The latter are decisive for how aggressively the bacterium behaves during an infection. There are virulence genes, for example, that the pathogen needs to invade the host cell. Because the process requires a lot of energy, bacteria only produce virulence factors when they are actually required. This precise timing control also minimises the risk that the bacteria are prematurely detected by the immune system.
The baton for correct timing
PinT acts as the baton which ensures the correct timing. Without the tiny molecule, the finely orchestrated tuning of virulence factors becomes disrupted. This shift in turn has a huge impact on the host cell. “In our study, nearly one tenth of all host genes were affected, which were now transcribed either more or less frequently compared to a normal infection,” Westermann explains. “The activation of certain immune genes, for instance, was much stronger than usual.”
For the first time, the simultaneous sequencing of pathogen and host RNA has allowed scientists to follow the complex chain of molecular events that occur during the course of an infection. “With comparably little effort, the method promises a wealth of new insights,” Professor Jörg Vogel explains. “For many bacterial genes, it has been virtually impossible so far to clarify their contribution to infection – we simply didn't have the proper methods. Now, there finally is a sensitive tool to study these genes. Dual RNA sequencing opens up a new dimension to infection research.” However, the method generates large amounts of data. Experts in computation biology at the Universities of Würzburg and Leipzig have developed new algorithms specifically for the study that allow the automatic processing of the RNA sequences at a sufficient speed.
Alexander J. Westermann, Konrad U. Förstner, Fabian Amman, Lars Barquist, Yanjie Chao, Leon N. Schulte, Lydia Müller, Richard Reinhardt, Peter F. Stadler & Jörg Vogel: Dual RNA-seq unveils noncoding RNA functions in host–pathogen interactions; Nature (DOI: 10.1038/nature16547)
Contact
Prof. Dr. Jörg Vogel, Institute for Molecular Infection Biology of the University of Würzburg
Phone: +49 931 31-82575, E-mail: joerg.vogel@uni-wuerzburg.de
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni-wuerzburg.deAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



