From allergens to anodes: Pollen derived battery electrodes
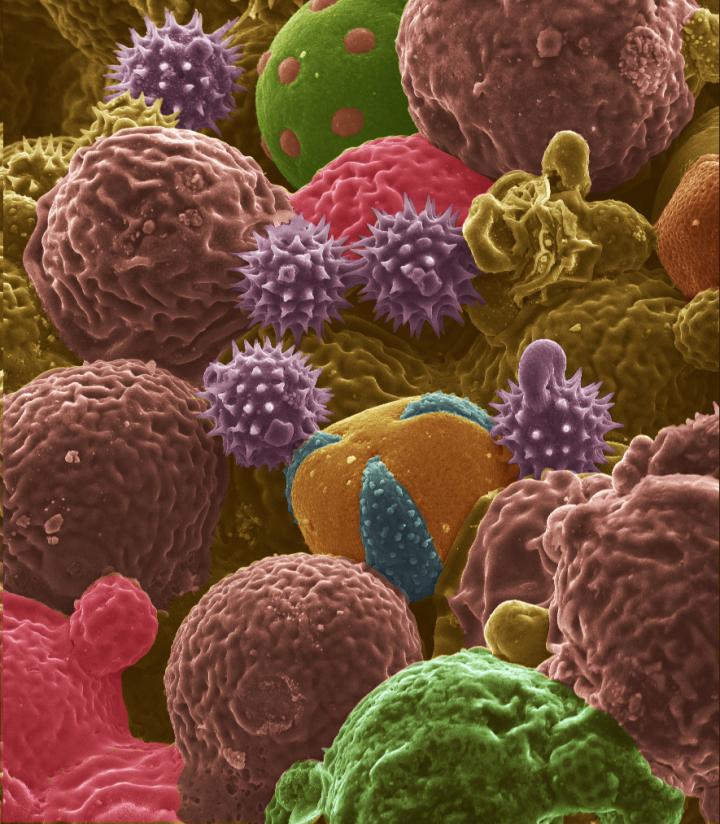
This scanning electron microscope image shows bee pollen studied for potential use as electrodes for lithium-ion batteries. Color was added to the original black-and-white image. (Purdue University image/ Jialiang Tang)
“Our findings have demonstrated that renewable pollens could produce carbon architectures for anode applications in energy storage devices,” said Vilas Pol, an associate professor in the School of Chemical Engineering and the School of Materials Engineering at Purdue University.
Batteries have two electrodes, called an anode and a cathode. The anodes in most of today's lithium-ion batteries are made of graphite. Lithium ions are contained in a liquid called an electrolyte, and these ions are stored in the anode during recharging.
The researchers tested bee pollen- and cattail pollen-derived carbons as anodes.
“Both are abundantly available,” said Pol, who worked with doctoral student Jialiang Tang. “The bottom line here is we want to learn something from nature that could be useful in creating better batteries with renewable feedstock.”
Research findings are detailed in a paper that appeared on Feb. 5 in Nature's Scientific Reports.
Whereas bee pollen is a mixture of different pollen types collected by honey bees, the cattail pollens all have the same shape.
“I started looking into pollens when my mom told me she had developed pollen allergy symptoms about two years ago,” Tang said. “I was fascinated by the beauty and diversity of pollen microstructures. But the idea of using them as battery anodes did not really kick in until I started working on battery research and learned more about carbonization of biomass.”
The researchers processed the pollen under high temperatures in a chamber containing argon gas using a procedure called pyrolysis, yielding pure carbon in the original shape of the pollen particles. They were further processed, or “activated,” by heating at lower temperature – about 300 degrees Celsius – in the presence of oxygen, forming pores in the carbon structures to increase their energy-storage capacity.
The research showed the pollen anodes could be charged at various rates. While charging for 10 hours resulted in a full charge, charging them for only one hour resulted in more than half of a full charge, Pol said. “The theoretical capacity of graphite is 372 milliamp hours per gram, and we achieved 200 milliamp hours after one hour of charging,” he said.
The researchers tested the carbon at 25 degrees Celsius and 50 degrees Celsius to simulate a range of climates.
“This is because the weather-based degradation of batteries is totally different in New Mexico compared to Indiana,” Pol said.
Findings showed the cattail pollens performed better than bee pollen.
The work is ongoing. Whereas the current work studied the pollen in only anodes, future research will include work to study them in a full-cell battery with a commercial cathode.
“We are just introducing the fascinating concept here,” Pol said. “Further work is needed to determine how practical it might be.”
Electron microscopy studies were performed at the Birck Nanotechnology Center in Purdue's Discovery Park.
###
Note to Journalists: The research paper is available from Emil Venere, 765-494-4709, venere@purdue.edu.
The work was supported by Purdue's School of Chemical Engineering. The electron microscopy studies at Birck were funded by a Kirk exploratory research grant and were conducted by doctoral students Arthur D. Dysart and Vinodkumar Etacheri. An XPS measurement was conducted by Dmitry Zemlyanov at Birck. Other support came from the Hoosier Heavy Hybrid Center of Excellence (H3CoE) fellowship, funded by U.S. Department of Energy.
Writer: Emil Venere, 765-494-4709, venere@purdue.edu
Source: Vilas G. Pol, 765-494-0044, vpol@purdue.edu
ABSTRACT
From Allergens to Battery Anodes: Nature-Inspired, Pollen Derived Carbon Architectures for Room-and Elevated-Temperature Li-ion Storage
Jialiang Tang & Vilas G. Pol *
School of Chemical Engineering, Purdue University
*E-mail: vpol@purdue.edu The conversion of allergic pollen grains into carbon microstructures was carried out through a facile, one-step, solid-state pyrolysis process in an inert atmosphere. The as-prepared carbonaceous particles were further air activated at 300 °C and then evaluated as lithium ion battery anodes at room (25 °C) and elevated (50 °C) temperatures. The distinct morphologies of bee pollens and cattail pollens are resembled on the final architecture of produced carbons. Scanning Electron Microscopy images shows that activated bee pollen carbon (ABP) is comprised of spiky, brain-like, and tiny spheres; while activated cattail pollen carbon (ACP) resembles deflated spheres. Structural analysis through X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy confirmed their amorphous nature. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis of ABP and ACP confirmed that both samples contain high levels of oxygen and small amount of nitrogen contents. At C/10 rate, ACP electrode delivered high specific lithium storage reversible capacities (590 mAh/g at 50 °C and 382 mAh/g at 25 °C) and also exhibited excellent high rate capabilities. Through electrochemical impedance spectroscopy studies, improved performance of ACP is attributed to its lower charge transfer resistance than ABP. Current studies demonstrate that morphologically distinct renewable pollens could produce carbon architectures for anode applications in energy storage devices.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

Compact LCOS Microdisplay with Fast CMOS Backplane
…for High-Speed Light Modulation. Researchers from the Fraunhofer Institute for Photonic Microsystems IPMS, in collaboration with HOLOEYE Photonics AG, have developed a compact LCOS microdisplay with high refresh rates that…

New perspectives for material detection
CRC MARIE enters third funding period: A major success for terahertz research: Scientists at the University of Duisburg-Essen and the Ruhr University Bochum have been researching mobile material detection since…

CD Laboratory at TU Graz Researches New Semiconductor Materials
Using energy- and resource-saving methods, a research team at the Institute of Inorganic Chemistry at TU Graz aims to produce high-quality doped silicon layers for the electronics and solar industries….



