Insect wings inspire antibacterial surfaces for corneal transplants, other medical devices
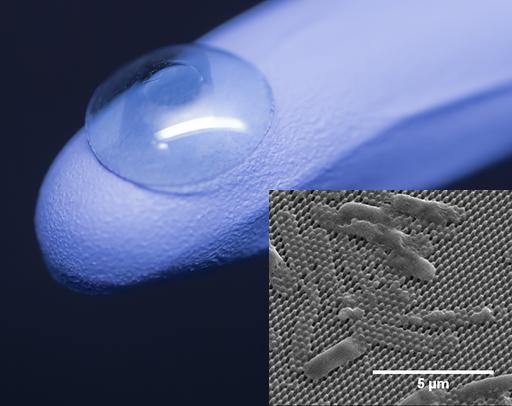
The center of an artificial cornea (on glove) is coated with tiny pillars that impale and kill bacterial cells (inset). Credit: Jonathan Pegan (cornea) and Mary Nora Dickson (inset)
The researchers present their work today at the 251st National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS, the world's largest scientific society, is holding the meeting here through Thursday. It features more than 12,500 presentations on a wide range of science topics.
“Other research groups have also created antibacterial nanopillar surfaces, but none of their approaches can be used on ordinary polymer surfaces or be scaled up easily,” according to Albert F. Yee, Ph.D., who leads a team working on the topic. By contrast, the production method his group is adapting overcomes these hurdles.
“Our method is based on one developed in the early 2000s for the semiconductor industry,” says Mary Nora Dickson, a graduate student in Yee's lab. “It is robust, inexpensive and can be used in industrial production. So it can now be applied to medical devices that could improve people's quality of life.”
One such application is an artificial cornea that Yee's group aims to construct from poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), familiar to many by trade names such as Plexiglas® and Lucite®. The material is already commonly used in medical devices including implantable intraocular lenses and traditional hard contact lenses. By building nanopillars into the surfaces of these types of devices, the researchers hope to make them bactericidal without the need for a separate biocidal coating or antibiotic drugs.
In earlier work, Yee, Dickson, Elena Liang, and colleagues at the University of California, Irvine, showed that their nanopillars, like those on cicada wings, can kill bacteria referred to as “gram-negative.” This group of microorganisms includes E. coli. But cicada nanopillars are unable to kill another type of bacteria known as “gram-positive” because these microbes have thicker cell walls. Wiping out these bacteria, which include MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) and Streptococcus (known as “strep”), is important because they cause infections on medical devices and in hospitals.
Compared to cicada nanopillars, the ones on dragonfly wings are taller and skinnier, and they can kill gram-positive bacteria. Now Dickson is trying to form these types of nanopillars on PMMA. However, she is finding that these structures are harder to replicate than the cicadas' stubby pillars. She is currently modifying the production process in several different ways to overcome these challenges.
For example, one version of the process uses commercial molds that contain billions of tiny pits in an area that covers just a few square inches. Pressing the mold onto a heated polymer film reshapes the film, leaving it decorated with nanopillars once the mold is removed. That method works just fine for the stubbier cicada-like pillars, but the finer dragonfly-like pillars tend to break apart when the mold is removed, much like over-cooked cupcakes sticking to the inside of an ungreased muffin tin.
So Dickson is experimenting with fluorinated silane coatings for the mold; these coatings could help free the pillars when it's time to remove the polymer film. She's also testing different chemical compositions for the mold itself.
Yee, Liang and Dickson are now applying their technique to curved surfaces such as an artificial cornea. For this application, Dickson created a flexible mold for the cicada-like pillars. She recently showed that the nanopillared PMMA surface produced with this curved mold retains the ability to kill bacteria without harming other kinds of cells in the eye. The team is currently developing a mold for the taller, dragonfly-type pillars.
The group has filed for patents on the bactericidal surface and artificial cornea application and hopes to begin animal trials this year.
###
A press conference on this topic will be held Tuesday, March 15, at 9:30 a.m. Pacific time in the San Diego Convention Center. Reporters may check-in at Room 16B (Mezzanine) in person, or watch live on YouTube http://bit.
Yee acknowledges funding from the University of California, Irvine, and from the Allergan Foundation.
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 158,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note to journalists: Please report that this research is being presented at a meeting of the American Chemical Society.
Title
Towards a Scalable, Biomimetic Antibacterial Polymer Surface
Abstract
Nanopillars on cicada wings are inherently antibacterial, irrespective of surface chemistry. Application of nanopillars to polymer surfaces would result in inherently antibacterial surfaces without use of antibiotic drugs or biocide chemicals. Nano- and microstructured antibacterial surfaces have been previously proposed; none of these approaches can be used on ordinary polymer surfaces or easily scaled up. Thus, we applied industrial polymer nanostructuring techniques to generate biomimetic antibacterial nanostructures at the surfaces of poly(methylmethacrylate) (PMMA), a material commonly used in medical devices. We employed nanoimprint lithography, an industrially viable fabrication process, to produce our nanostructures. We utilized several molds for our process: a nano-holed (negative) mold, a commercially available nickel antireflective nanopillar (positive) mold, and a black silicon nanopillar (positive) mold fabricated with reactive ion etching. We treated these oxide surfaces with a fluorinated silane release coating (perflurodecyltrichlorosilane) using molecular vapor deposition. These molds were used to fabricate PMMA nanopillar arrays or to generate polydimethylsiloxane nanohole arrays to be used for subsequent PMMA nanopillar molding. The replication processes resulted in large, flat PMMA nanopillar arrays. Compared to flat films, PMMA nanopillar arrays 1) exhibited reduced surface adhesion of live E. coli determined by a standard fluorescence based viability assay, and 2) killed these bacteria, as evidenced AFM and SEM showing punctured bacterial cells on nanopillar arrays. Recent efforts have focused on optimizing the bactericidal performance of pillars to assess effectiveness against gram-positive bacteria. Our surfaces could be used for a wide variety of environmental and medical applications.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



