Cost efficient Diode Lasers for Industrial Applications
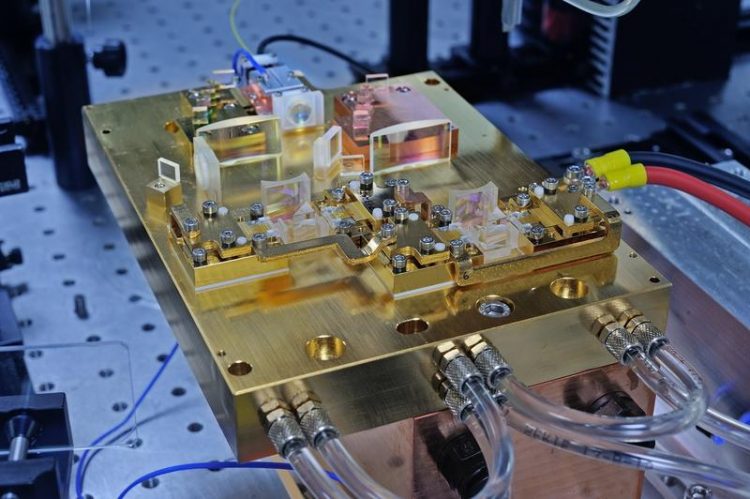
DWDM prototype consisting of actively cooled DFB mini-bars. Fraunhofer ILT, Aachen.
Seven partners for various scientific issues
Design and technological development of high performance diode lasers was performed by three partners within BRIDLE. First, the Ferdinand-Braun-Institut für Höchstfrequenztechnik im Forschungsverbund Berlin e.V. (FBH) developed novel epitaxial designs and process technology.
Those developments enabled the use of broad area mini bars with a narrow stripe width of only 30 µm to operate with a brightness that is increased by at least a factor of two in comparison with state of the art chips with a 100 µm stripe width. Furthermore, highly brilliant narrow-stripe DFB diode lasers with monolithically-integrated surface gratings were developed and optimized to simultaneously deliver narrow spectrum (< 1nm), high power (5W), high efficiency (50%) within a low beam parameter product (< 2mm-mrad) for the first time.
For coherent coupling experiments, monolithically grating-stabilized tapered diode lasers were developed, with record (54%) conversion efficiency. Second, ridge waveguide diode lasers for coherent coupling experiments were developed by Modulight Inc., which deliver an output power of 1 W per emitter. Finally, design optimization was supported through detailed simulation work performed by University of Nottingham (UNott).
Based on the high brightness diode laser mini bars developed within the BRIDLE project, DILAS was able to simplify its well-known T-bar concept for 105 µm fibre coupling. Furthermore DILAS could increase the optical output power up to 300 W ex 100 µm. The modules wavelength’can be stabilized and used for dense wavelength multiplexing to further increase output power and brightness. The assembly process is fully automated.
Fraunhofer Institute for Laser Technology ILT analyzed and compared different techniques for dense wavelength multiplexing. These techniques include different approaches based on surface gratings, simultaneous wavelength stabilization and multiplexing by use of dielectric filters and VBGs as well as DWDM of wavelength chirped DFB diode lasers by dielectric filters. Filters from different international manufacturers were tested thoroughly. For the first time, Fraunhofer ILT has developed concepts which can be used to implement and test compact modules in the medium power range of 10 W to 100 W output power, with a fiber having a core diameter of 35 µm and a numerical aperture of 0.2. 46 W were realized experimentally. A 7:1 fiber combiner (35/105 µm) was developed for further power scaling.
Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique/Institut d’Optique (CNRS-IO) demonstrated a new architecture for passive coherent combining of diode laser with ridge lasers (delivered by Modulight) and tapered lasers (delivered by FBH). The set-up is based on the separation of the phase-locking stage, which takes place in an external cavity on the rear side of the lasers, and the beam combining stage ,which is achieved outside the cavity on their front side. This configuration demonstrates successively a combined power up to 7.5 W in a single beam from a bar of five high-brightness emitters, using a specifically designed diffractive combiner. Furthermore, the active coherent combining of five tapered amplifiers achieved a power of more than 11 W with a combining efficiency of 76%.
The University of Nottingham developed software tools that enable the investigation of coupling between external optics and the diode laser itself. These tools can be used to better understand coherent coupling, wavelength stabilization or parasitic back reflections. UNott developed a dynamic laser simulation tool for CBC diode laser systems. This tool is used in conjunction with external cavity models developed at CNRS-IO to investigate the nature and dynamics of the phase locking mechanisms in CBC laser systems. Furthermore, UNott’s laser simulation tool Speclase was coupled to external optical design software (ZEMAX®) for external cavity simulations at the subsystem level.
Industrial applications of the developed prototypes are investigated by Bystronic Laser AG and Fraunhofer ILT. For instance, lasers manufactured by DILAS are used for Selective Laser Melting of metals at Fraunhofer ILT.
For more information visit the BRIDLE project website ( www.bridle.eu )
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



