Making magnets flip like cats at room temperature
Flipping NiMnSb magnet ill.:/©: Inspire Group, JGU
In today’s world of ever-increasing digital information storage and computation, the next information storage revolution seeks to exploit a novel effect arising from the relativistic physics of Einstein which allows to make a new type of magnet behave like cats.
Similar to the ability of a cat to flip itself in the air by twisting different parts of its body in different directions and land on its feet, these magnets can flip themselves through the internal motion of their own electrons.
“In these new magnetic materials, a current running through the magnet can turn around the direction of the magnetization depending on the direction of the current,” explained Professor Jairo Sinova of the Institute of Physics at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU).
“This novel phenomenon in physics, dubbed spin-orbit torques, links the spin-degree of freedom of magnets which gives rise to the magnetization to the charge degree of freedom that allows for current-charge motion inside the material.
This novel effect has been pioneered, among others, by recent predictions by the Sinova group in Mainz together with theoretical and experimental collaborators. It occurs in magnetic materials that have broken-inversion symmetry.
The researchers first observed spin-orbit torques in the artificial bulk diluted magnetic semiconductor GaMnAs. GaMnAs is the diluted counterpart of crystalline zincblende structures of Silicon and Gallium arsenide, which are the pillars of modern electronics. However, in GaMnAs, spin-orbit torques were demonstrated only at very low temperatures.
In collaboration with an international team of researchers from Prague, Cambridge, Würzburg, Jülich, and Nottingham, Professor Jairo Sinova and his Ph.D. students Jacob Gayles and Libor Šmejkal now have published their findings, which could pave the way for using spin-orbit torques in technological applications.
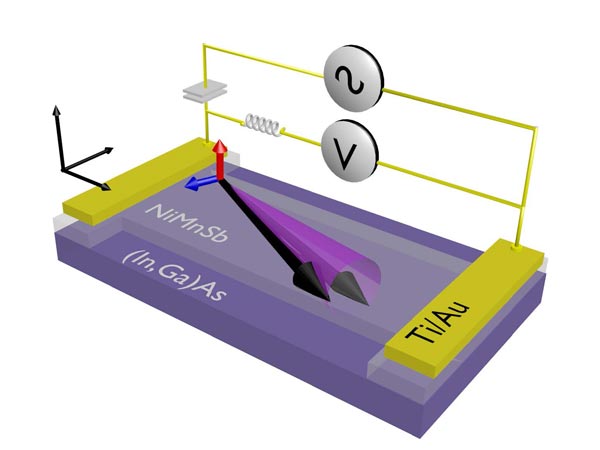
Thanks to the synergetic teamwork of theorists and experimentalists, the researchers were able to predict and demonstrate the effect of spin-orbit torques in NiMnSb crystal at room temperature. NiMnSb was chosen according to the systematic analysis of the symmetry the crystal point groups in conjunction with microscopic first principles calculations of the effect.
All electrical ferromagnetic resonance measurements were then used to detect the room-temperature spin-orbit torques in NiMnSb microbars. Being able to use single magnet manipulation at room temperature represents an important step towards improved magnetic random access memory architectures for technical applications that are all fully electrical, highly scalable, and require low power.
Publication:
C. Ciccarelli, L. Anderson et al.
Room-temperature spin-orbit torque in NiMnSb
Nature Physics, 16 May 2016
DOI: 10.1038/nphys3772
Illustration:
http://www.uni-mainz.de/bilder_presse/08_physik_komet_nimnsb.jpg
Flipping NiMnSb magnet
ill.:/©: Inspire Group, JGU
Further information:
Professor Dr. Jairo Sinova
Spintronics and Nanoelectronics Theory Group
Institute of Physics
Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz
55099 Mainz, GERMANY
phone +49 6131 39-23646
fax +49 6131 39-23474
e-mail: sinova-group@uni-mainz.de
http://www.sinova-group.physik.uni-mainz.de/
http://www.nature.com/nphys/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nphys3772.html – Publication ;
http://www.uni-mainz.de/presse/59190.php – press release “Jairo Sinova receives ERC funding to develop new spintronic concepts” (22 January 2014)
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

A ‘language’ for ML models to predict nanopore properties
A large number of 2D materials like graphene can have nanopores – small holes formed by missing atoms through which foreign substances can pass. The properties of these nanopores dictate many…

Clinically validated, wearable ultrasound patch
… for continuous blood pressure monitoring. A team of researchers at the University of California San Diego has developed a new and improved wearable ultrasound patch for continuous and noninvasive…

A new puzzle piece for string theory research
Dr. Ksenia Fedosova from the Cluster of Excellence Mathematics Münster, along with an international research team, has proven a conjecture in string theory that physicists had proposed regarding certain equations….



