Amazon forests: Biodiversity can help mitigate climate risks
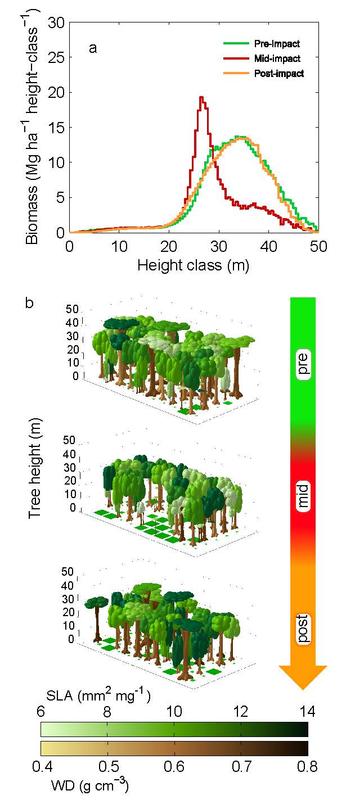
Figure 3 PIK
“Plant trait diversity may enable the Amazon forests, the world’s greatest and maybe most fascinating tropical ecosystem, to adjust to some level of climate change – certain trees dominant today could decrease and their place will be taken by others which are better suited for the new climate conditions in the future,” says Boris Sakschewski from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), lead-author of the study to be published in Nature Climate Change.
Tree survival for instance depends on what the scientists call ‘leaf economics’: their different size, thickness, longevity or density defines how well the plant can deal with higher temperatures and water scarcity. “Biodiversity shows not to be a nice-to-have but indeed a must-have,” says Sakschewski. “We find it could be functional for the long-term survival of Earth’s large reservoirs of biomass, such as the forests of the Amazon region.”
However, this depends on the level of stress. Only in a scenario of moderate climate change, high biodiversity can, after a sharp decline of biomass, contribute to substantial recovery in vast areas across the Amazon region after a few hundred years. Here, more than 80 percent of the Amazon area would show substantial regrowth, according to the study. In contrast, in a business-as-usual scenario of greenhouse-gas emissions leading to massive climate change, less than 20 percent of the area would show this positive effect.
A significant step forward in Earth system modelling
Never before have these dynamics been integrated in a biogeochemical vegetation simulation of climate effects, so this is a significant step forward in Earth system modelling. “To explain how plant trait diversity contributes to the resilience of rainforest we first investigated an experimental site in Ecuador and then extended the simulations to the Amazon basin,” says team leader Kirsten Thonicke from PIK. “We’ve been working on this for years. While it is well-known that biodiversity is relevant for ecosystem productivity and biomass storage, up to now it could not be shown in a large-scale quantitative way. We’re glad to advance previous research by closing this important gap.”
“This is good news for the Amazon forest – still, it doesn’t mean that climate change would not harm this unique ecosystem substantially, quite the contrary,” says Wolfgang Lucht, co-chair of PIK’s research domain Earth System Analysis. While high biodiversity enables the forest to eventually regain much of its biomass, there is a huge disruption in the transition and the species composition would be different afterwards even under moderate global warming. “Despite the encouraging findings on biodiversity’s functional value, the Amazon rainforest unfortunately remains one of the critical hotspots on the planet that demand very rapid decreases in CO2 emissions.”
Article: Sakschewski, B., von Bloh, W., Boit, A., Poorter, L., Peña-Claros, M., Heinke, J., Joshi, J., Thonicke, K. (2016): Resilience of Amazon forests emerges from plant trait diversity. Nature Climate Change (Advance Online Publication) [DOI:10.1038/nclimate3109]
Link to the article once it is published: http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nclimate3109
Link to short video and explanation: http://www.pik-potsdam.de/~borissa/video3454/
High-resolution figures from the paper are available upon individual request
For further information please contact:
PIK press office
Phone: +49 331 288 25 07
E-Mail: press@pik-potsdam.de
Twitter: @PIK_Climate
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



