Preferential trade agreements enhance global trade at the expense of its resilience
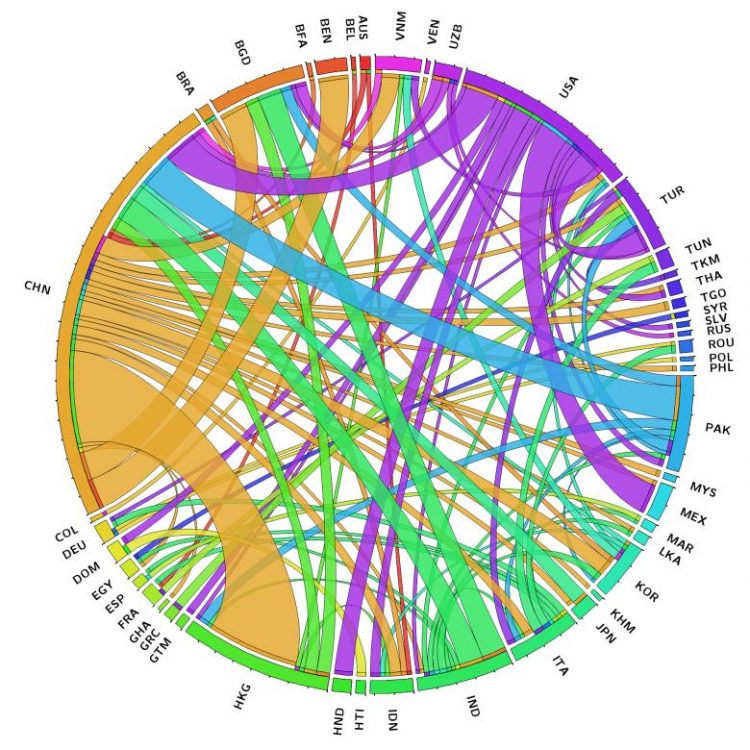
Global trade of cotton (HS 52) in 2009; only 49 countries with trade above $ 100 million USD are depicted. Names of countries are represented by the ISO 3166 standard three letter code. Kharrazi et al, 2017
Bi- and multilateral trade agreements can make commodity trade networks more efficient and lead to more rapid growth of the volume of trade, but these gains come at the expense of resilience to economic shocks, such as the 2009 global financial crisis which decimated economies around the world. A new study published in the journal PLOS ONE makes use of the similarities between ecosystems and commodity trade networks to explore these phenomena.
“There is a fundamental trade-off between efficiency and growth, on one hand, and redundancy and resilience of growth on the other,” says University of Tokyo researcher Ali Kharrazi, who started the work as a participant in the 2012 Young Scientists Summer Program at the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA).
Global commodity trade networks are increasingly complex dynamic systems, affected also by bilateral agreement between countries as well as broad regional trade agreements. Traditional economic methods struggle to account for the complexity of these interactions and their role in defining the resilience of trade. In the new study, Kharrazi and researchers at IIASA applied an approach first developed to study ecological networks in order to better understand the dynamics and properties of the global commodity trade system.
“In this study, for the first time, we demonstrate empirically how redundancy and efficiency in global trade networks can make them resilient to global economic shock, while sustaining both long- and short-term growth,” says IIASA Advanced Systems Analysis Program Director Elena Rovenskaya, who contributed to the study.
“Local and global shocks, such as economic and financial crises, political instability, and environmental disasters require strategies to increase our capacity for resilience,” says Kharrazi, “Policy and decision making should consider both the short and long term growth and resilience of growth based on inclusivity or exclusivity and intensity of trading partners from a network perspective.”
The researchers point out that resilience and growth are not the only targets that should be considered in economic policymaking, adds Brian Fath, a researcher at IIASA and Towson University in the USA who also worked on the study. He says, “While our study showed growth is not hindered by redundancy, resilience of growth is not the only metric to consider in a healthy community. The merits of continued trade growth should be evaluated based on the three economic, environmental, and social pillars of sustainable development.”
Reference
Kharrazi A, Rovenskaya E, Fath BD (2017). Network Structure Impacts Global Commodity Trade Growth and Resilience. PLOS ONE http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0171184
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Business and Finance
This area provides up-to-date and interesting developments from the world of business, economics and finance.
A wealth of information is available on topics ranging from stock markets, consumer climate, labor market policies, bond markets, foreign trade and interest rate trends to stock exchange news and economic forecasts.
Newest articles

A ‘language’ for ML models to predict nanopore properties
A large number of 2D materials like graphene can have nanopores – small holes formed by missing atoms through which foreign substances can pass. The properties of these nanopores dictate many…

Clinically validated, wearable ultrasound patch
… for continuous blood pressure monitoring. A team of researchers at the University of California San Diego has developed a new and improved wearable ultrasound patch for continuous and noninvasive…

A new puzzle piece for string theory research
Dr. Ksenia Fedosova from the Cluster of Excellence Mathematics Münster, along with an international research team, has proven a conjecture in string theory that physicists had proposed regarding certain equations….



