Detailed chemical structure of P22 virus resolved
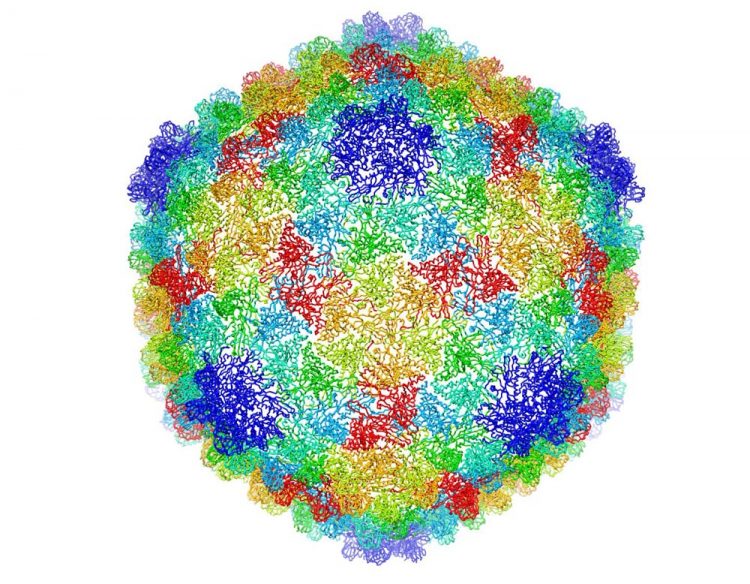
Complete capsid of bacteriophage P22 generated with validated atomic models that were derived from the high-resolution cryoEM density map. Credit: C.Hryc and the Chiu Lab
For nearly 30 years the laboratory of Dr. Wah Chiu, Distinguished Service Professor and Alvin Romansky Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at Baylor and senior author of the paper, has been applying electron cryomicroscopy and computer reconstruction techniques to determine the 3-D structures of biological nanomachines, such as the P22 virus.
This virus is a bacteriophage — a type that infects bacteria, in this case Salmonella -and has been extensively studied through genetics, biochemistry and biophysics. Nevertheless, its precise chemical structure has remained unresolved.
“In 2011, we published a structure of the P22 virus that allowed us to trace out a majority of the protein backbone with certainty, but we could not visualize the fine details, such as individual, small side chains,” said co-first author Corey Hryc, graduate student in the Chiu lab.
“Since then, the technology in the microscopes has improved; we have new detectors that allow us to record better- and higher-contrast images to improve the resolution of our data. In addition, we have new processing algorithms that allow us to increase our ability to resolve the structure.”
A new era of precision cryo-electron microscopy
“The novelty of this work is that we took more than 20,000 two-dimensional individual images of the P22 virus with the electron cryomicroscope and combined them using computational protocols to produce a 3-D map with unprecedented detail,” Chiu said.
“By comparison, the two-dimensional images we take of the virus would be like taking thousands of photos of your head randomly, in different places, and then fit the photos where they would belong in a 3-D space using a computer,” Hryc said. “In this way, we could probably create a 3-D model of your head, and, if the photos were X-ray images, we could see the insides, too.”
The analysis of the high-resolution map of the P22 virus allowed the researchers to see in great detail all the building blocks of the proteins in the virus, the amino acids, including their side chains and how they interact with neighbor amino acids.
“The minute details we obtain now of biological structures with this approach give us more information about their biochemistry than before,” Hryc said. “I think that's exciting.”
“Thanks to this exquisite structural detail, we have determined the protein chemistry of the P22 virus,” Chiu said. “I think it is important that we provide detailed annotations with the structure so other researchers can use it for their future experiments.”
“Without the annotations you would think that everything in the map is essentially equivalent from a modeling standpoint, but this is not the case,” Hryc said. “Some of these amino acids are much more clearly visible than others, particularly in the interactions between the different components of the virus.”
“Hryc has set the standard for precision cryo-electron microscopy,” Chiu said.
###
Other contributors to this work include co-first author Dong-Hua Chen currently at Stanford University, Pavel V. Afonine, Joanita Jakana, Zhao Wang, Cameron Haase-Pettingell, Wen Jiang, Paul D. Adams, Jonathan A. King and Michael F. Schmid.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (P41GM103832, R01GM079429, P01GM063210 and PN2EY016525), the Robert Welch Foundation (Q1242) and The National Library of Medicine Training Program in Biomedical Informatics (Grant T15LM007093) awarded to the Keck Center of the Gulf Coast Consortia.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



