Igniting a solar flare in the corona with lower-atmosphere kindling
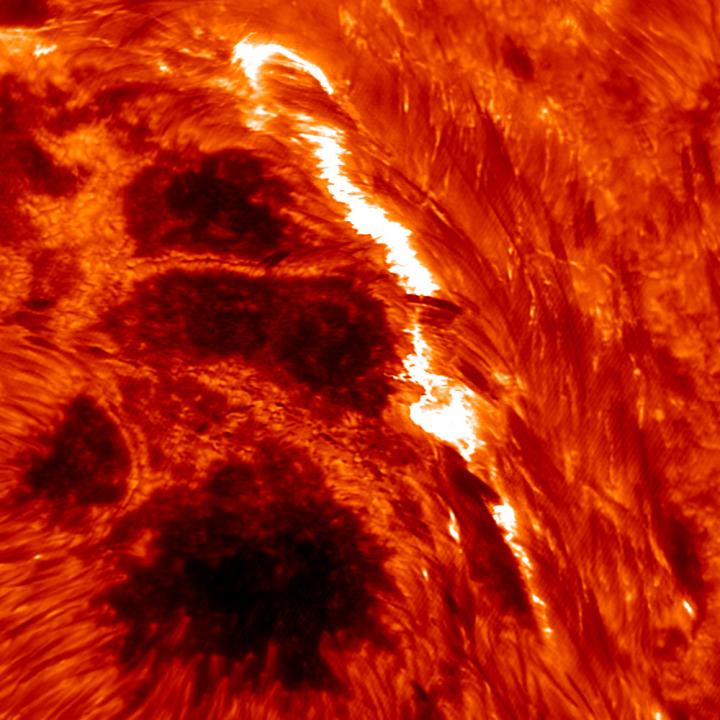
Recent images captured by NJIT's 1.6-meter New Solar Telescope at Big Bear Solar Observatory (BBSO) have revealed the emergence of small-scale magnetic fields in the lower reaches of the corona the researchers say may be linked to the onset of a main flare. Creditj: NJIT
Recent images captured by the university's 1.6-meter New Solar Telescope at Big Bear Solar Observatory (BBSO) have revealed the emergence of small-scale magnetic fields in the lower reaches of the corona the researchers say may be linked to the onset of a main flare. The study also includes the first scientific contributions from NJIT's newly commissioned Extended Owens Valley Solar Array (EOVSA).
“These smaller magnetic fields appear as precursors to the flare by reconnecting with each other – breaking apart and forming new connections – in an already stressed magnetic environment. This sets the stage for a larger energy release,” notes Haimin Wang, distinguished professor of physics at NJIT and the leading author of a paper published this week in the magazine Nature Astronomy. The study, funded by the National Science Foundation and NASA, was conducted in collaboration with colleagues in Japan and China.
“Through our measurements, we are able to see the emergence of fine magnetic channel structures prior to the flare, which contain mixed positive and negative magnetic polarities,” Wang adds. “We then see a strong twist in the magnetic lines that creates instability in the system and may trigger the eruption.”
While solar flares are generally believed to be powered by what is known as free energy – energy stored in the corona that is released by twisting magnetic fields – the authors suggest that the build-up of coronal energy in the upper atmosphere alone may not be sufficient to trigger a flare. In their study of a prolonged flare on June 22, 2015, they observed in unprecedented detail the emergence in the lower atmosphere of what they call precursors, or “pre-flare brightenings,” in various wavelengths.
There are well-documented periods in which flares occur more frequently than the norm, but it has been difficult thus far to determine exactly when and where a particular flare might be initiated. The BBSO's recent study of a flare's magnetic evolution, enhanced by simultaneous microwave observations from EOVSA, has been able to pin down the time and location of the magnetic reconnection prior to the flare.
“Our study may help us predict flares with more precision,” Wang says.
A co-author of the article, Kanya Kusano of Nagoya University, compared BBSO's observations with his numerical simulation of the triggering process of solar flares.
“I found that the observational result is very well consistent with the simulation,” he notes. “This clearly indicates that these mixed-polarity magnetic channel structures are typical of the stressed magnetic field that triggers solar flares.”
###
About NJIT
One of the nation's leading public technological universities, New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT) is a top-tier research university that prepares students to become leaders in the technology-dependent economy of the 21st century. NJIT's multidisciplinary curriculum and computing-intensive approach to education provide technological proficiency, business acumen and leadership skills. With an enrollment of 11,400 graduate and undergraduate students, NJIT offers small-campus intimacy with the resources of a major public research university. NJIT is a global leader in such fields as solar research, nanotechnology, resilient design, tissue engineering, and cybersecurity, in addition to others. NJIT is among the top U.S. polytechnic public universities in research expenditures, exceeding $130 million, and is among the top 1 percent of public colleges and universities in return on educational investment, according to PayScale.com. NJIT has a $1.74 billion annual economic impact on the State of New Jersey.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

A ‘language’ for ML models to predict nanopore properties
A large number of 2D materials like graphene can have nanopores – small holes formed by missing atoms through which foreign substances can pass. The properties of these nanopores dictate many…

Clinically validated, wearable ultrasound patch
… for continuous blood pressure monitoring. A team of researchers at the University of California San Diego has developed a new and improved wearable ultrasound patch for continuous and noninvasive…

A new puzzle piece for string theory research
Dr. Ksenia Fedosova from the Cluster of Excellence Mathematics Münster, along with an international research team, has proven a conjecture in string theory that physicists had proposed regarding certain equations….



