Hannover Messe: New hybrid inks for printed, flexible electronics without sintering
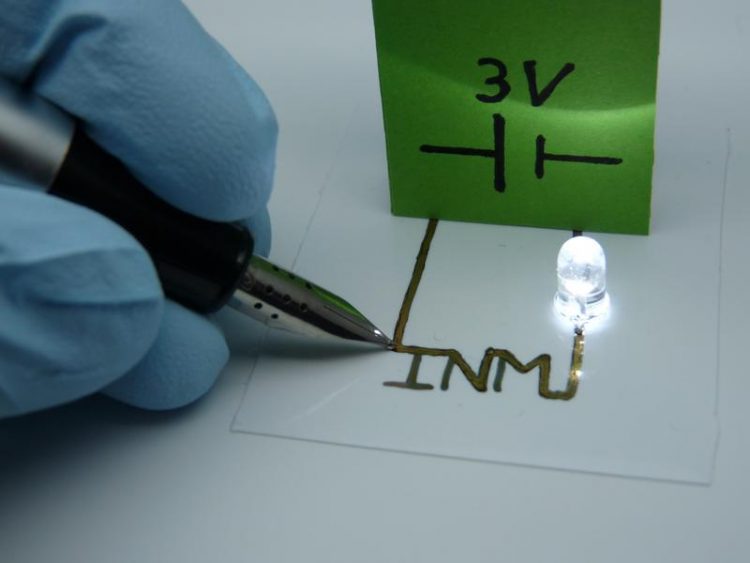
New type of hybrid inks allow electronic circuits to be applied to paper directly from a pen. Sourec: INM, free within this press release
Flexible circuits can be produced inexpensively on foil or paper using printing processes and permit futuristic designs with curved diodes or input elements. This requires printable electronic materials that retain a high level of conductivity during usage in spite of their curved surfaces.
Research scientists at INM – Leibniz Institute for New Materials have now developed a new type of hybrid inks which allows electronic circuits to be applied to paper directly from a pen, for example. They are usable after drying without any further processing.
The developers will be demonstrating their results and the possibilities they offer at stand B46 in hall 2 at this year's Hannover Messe which takes place from April 24 to April 28.
To create their hybrid inks, the scientists combined the benefits of polymers and metallic nanoparticles: gold or silver nanoparticles are coated with organic, conductive polymers and are then suspended in mixtures of water and alcohol.
“Metal nanoparticles with ligands are already today printed to form electronics circuits,” explains the materials scientist Kraus, adding that the shells mostly had to be removed by a sintering process. While the shells control the arrangement of the nanoparticles, they impede conductivity.
He added that this was difficult in the case of carrier materials that are sensitive to temperature such as paper or polymer films since these would be damaged during the sintering process. Kraus summarizes the results of his research, saying, “Our new hybrid inks are conductive in the as-dried state, are mechanically flexible, and do not require sintering”.
In their hybrid inks, the organic compounds have three functions: “The compounds serve as ligands, ensuring that the nanoparticles remain suspended in the liquid mixture; any agglomeration of particles would have a negative effect on the printing process. Simultaneously, the organic ligands ensure that the nanoparticles have a good arrangement when drying.
Ultimately, the organic compounds act as ´hinges´: if the material is bent, they maintain the electrical conductivity. In a layer of metal particles without the polymer sheath, the electrical conductivity would be quickly lost on bending,” Kraus continues.
Due to the combination of both materials, when bent, the electrical conductivity is greater than in a layer that is made purely of conductive polymer or a layer made purely of metal nanoparticles.
Your expert at INM
Prof. Dr. Tobias Kraus
INM – Leibniz-Institute for New Materials
Head Structure Formation
Deputy Head Innovation Center INM
Phone: +49 681-9300-389
tobias.kraus@leibniz-inm.de
INM – Leibniz Institute for New Materials, situated in Saarbrücken, is an internationally leading centre for materials research. INM conducts research and development to create new materials – for today, tomorrow and beyond. Research at INM is performed in three fields: Nanocomposite Technology, Interface Materials, and Bio Interfaces. INM is an institute of the Leibniz Association and has about 240 employees.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Trade Fair News
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



