Fungi have enormous potential for new antibiotics
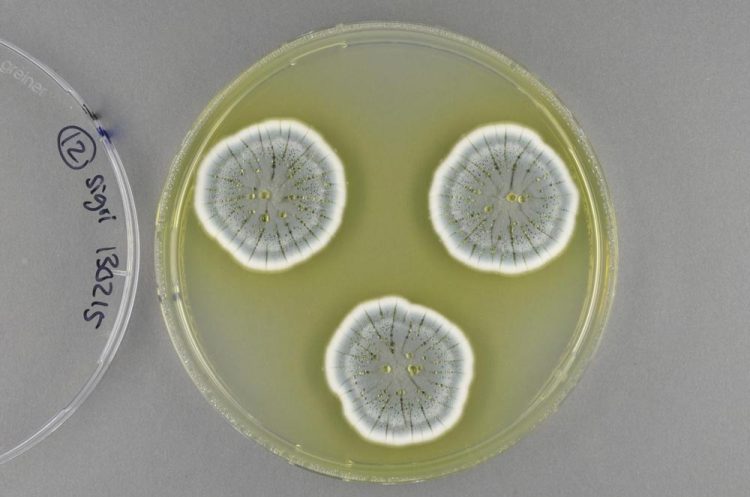
While Penicillia are already industrially used in the production of antibiotics, other pharmaceuticals, industrial enzymes and in the manufacturing of food products, new research reveals that their potential for production of novel antibiotics is far from exhausted. Penicillia are naturally found in temperate climates growing on organic matter, including soil, plant material, dung and food products. The isolation of novel bioactive compounds from these species might encompass a source of new antibiotics to fight infectious microorganisms. Credit: Jens Christian Nielsen
Antibiotics have saved millions of lives since they were discovered in the 1940s. But recently we've had to learn a new term: antibiotic resistance. More and more bacteria are developing their own protection against antibiotics, thereby becoming resistant to treatment. This will lead to simple infections becoming lethal once again. Our need for new antibiotics is urgent.
The first antibiotic to be mass-produced was penicillin, derived from Penicillium fungi. In their quest for new antibiotics, Chalmers researchers sequenced the genomes of nine different types of Penicillium species. And the findings are amazing:
“We found that the fungi have enormous, previously untapped, potential for the production of new antibiotics and other bioactive compounds, such as cancer medicines,” says Jens Christian Nielsen, a PhD student at the Department of Biology and Biological Engineering.
He works in a research team led by another Chalmers researcher with almost the same name: Professor Jens Nielsen.
In the study, recently published in the journal, Nature Microbiology, the research group scanned the genomes of 24 different kinds of fungi to find genes responsible for the production of various bioactive compounds, like antibiotics. More than 1000 pathways were discovered, showing immense potential for fungi to produce a large variety of natural and bioactive chemicals that could be used as pharmaceuticals.
In about 90 cases, the researchers were able to predict the chemical products of the pathways. As evidence of this, they followed the production of the antibiotic, yanuthone, and identified new fungi able to produce the compound, but also that some species could produce a new version of the drug.
All in all, the study shows vast potential for fungi, not only in producing new antibiotics but also in enabling more efficient production of existing ones – and maybe also more effective versions of the existing ones.
“It's important to find new antibiotics in order to give physicians a broad palette of antibiotics, existing ones as well as new ones, to use in treatment. This will make it harder for bacteria to develop resistance,” explains Jens Christian Nielsen.
“Previous efforts to find new antibiotics have mainly focused on bacteria. Fungi have been hard to study – we know very little of what they can do – but we do know that they develop bioactive substances naturally, as a way to protect themselves and survive in a competitive environment. This made it logical to apply our research tools to fungi.”
Researchers now have various paths to follow. One way of moving forward could be to look further at the production of the new yanuthone compound. The Chalmers researchers have also drawn up a map that makes it possible to compare hundreds of genes in the continuous evaluation of bioactive products with potent drugs in sight.
How long it would take to launch new antibiotics on the market is impossible to say.
“Governments need to act. The pharmaceutical industry doesn't want to spend money on new antibiotics, it's not lucrative. This is why our governments have to step in and, for instance, support clinical studies. Their support would make it easier to reach the market, especially for smaller companies. This could fuel production,” says Jens Christian Nielsen.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

A new puzzle piece for string theory research
Dr. Ksenia Fedosova from the Cluster of Excellence Mathematics Münster, along with an international research team, has proven a conjecture in string theory that physicists had proposed regarding certain equations….

Climate change can cause stress in herring larvae
The occurrence of multiple stressors undermines the acclimatisation strategies of juvenile herring: If larvae are exposed to several stress factors at the same time, their ability to respond to these…

Making high-yielding rice affordable and sustainable
Plant biologists show how two genes work together to trigger embryo formation in rice. Rice is a staple food crop for more than half the world’s population, but most farmers…



