Researchers Discover a Potential New Target for Cancer Treatment
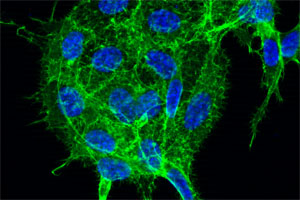
Depicted are lung cancer cells stained for the cytoskeleton (colored in green) and the nuclei (colored in blue). A new therapeutic method may be able to reduce the growth and aggressiveness of these cells. Source: Florian Weinberg
Dr. Florian Weinberg, from Prof. Dr. Tilman Brummer’s research group at the Institute of Molecular Medicine and Cell Research (IMMZ) of the University of Freiburg, joined forces with scientists from the Departments of Clinical Pathology and Medicine I of the University Medical Centre Freiburg and the Kinghorn Cancer Centre/Garvan Insitute in Australia in an international team that has identified a new target for cancer therapy.
The researchers discovered that the enzyme RIOK1 collaborates with the RAS protein, which is often mutated in tumors and therefore promotes tumor growth and the development of metastases. These secondary tumors are spread by the primary tumor, if it is not removed in time, and are the cause of death in most cancer patients.
The researchers believe it may be possible to use so-called inhibitors to block the enzymatic activity of RIOK1, thereby slowing down the disease’s progression. The team has recently published its findings in the translational journal EBioMedicine.
Cancer diseases are characterized by gene mutations that cause the uncontrolled growth of the body's own cells. This, in turn, results in the development of tumors. Most treatments combine surgery to remove the tumor with chemotherapy or radiation therapy, both of which are used to inhibit the fast growth of cells. Specific inhibitors can also be used as an additional or alternative therapy.
These drugs inhibit the activity of the harmful proteins and enzymes produced by the mutated genes in tumors. However, there are currently only very few ways to specifically treat RAS-driven tumors. Because roughly 30 percent of all cancer patients carry a Ras mutation in their tumors, there is a very strong need to find new ways to target RAS.
The team of scientists studied the growth behavior of human RAS-mutated lung-, breast-, and colorectal cancer cells in cell culture and animal models. In each case, they were able to genetically modify the cells, so that they were no longer able to produce RIOK1, a method that mimics the effects of a still to be developed RIOK1 inhibitor. By this approach, the authors were able to reduce the growth and aggressiveness of the cancer cells.
Especially in the animal models, the researchers observed that the modified cells were no longer able to form metastases. RIOK1 belongs to the enzyme family of protein kinases for which inhibitors are already successfully used in cancer therapy. Therefore, the scientists believe that similar substances inhibiting the enzymatic activity of RIOK1 could be developed in the near future. In addition, RIOK1 could be used to predict the progression of lung and breast cancer more accurately, as the researchers observed an increased production of RIOK1 in the tumor tissue of patients who had a poorer prognosis.
The researchers stated that more studies are needed to confirm RIOK1 as a target for cancer therapy, however. It would be important, for example, to understand the exact mechanism through which the enzyme supports cancer growth and metastasis.
It is also essential that inhibitors be tested first on model organisms before the drugs can be tested in clinical studies. The researchers’ initial studies on roundworms and human cells have demonstrated that healthy body cells are either only partially affected or not affected at all by the loss of RIOK1, because they do not depend on the enzyme. This would mean that, at the same time, cancer cells would be inhibited from growing and from spreading new tumors.
The study was funded by the Cluster of Excellence BIOSS Centre for Biological Signalling Studies and the Collaborative Research Center 850 “Control of Cell Motility in Morphogenesis, Cancer Invasion and Metastasis” at the University of Freiburg.
Caption:
Depicted are lung cancer cells stained for the cytoskeleton (colored in green) and the nuclei (colored in blue). A new therapeutic method may be able to reduce the growth and aggressiveness of these cells.
Source: Florian Weinberg
Original Publication:
The Atypical Kinase RIOK1 Promotes Tumor Growth and Invasive Behavior.
Florian Weinberg, Nadine Reischmann, Lisa Fauth, Sanaz Taromi, Justin Mastroianni, Martin Köhler, Sebastian Halbach, Andrea C. Becker, Niantao Deng, Tatjana Schmitz, Franziska Maria Uhl, Nicola Herbener, Bianca Riedel, Fabian Beier, Alexander Swarbrick, Silke Lassmann, Jörn Dengjel, Robert Zeiser, Tilman Brummer
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.04.015
Contact:
Prof. Dr. Tilman Brummer
Institute of Molecular Medicine and Cell Research
University of Freiburg
Phone: +49 (0)761 / 203 – 9610
E-Mail: tilman.brummer@zbsa.de
https://www.pr.uni-freiburg.de/pm-en/2017/researchers-discover-a-potential-new-t…
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

A ‘language’ for ML models to predict nanopore properties
A large number of 2D materials like graphene can have nanopores – small holes formed by missing atoms through which foreign substances can pass. The properties of these nanopores dictate many…

Clinically validated, wearable ultrasound patch
… for continuous blood pressure monitoring. A team of researchers at the University of California San Diego has developed a new and improved wearable ultrasound patch for continuous and noninvasive…

A new puzzle piece for string theory research
Dr. Ksenia Fedosova from the Cluster of Excellence Mathematics Münster, along with an international research team, has proven a conjecture in string theory that physicists had proposed regarding certain equations….



