How cells combat Salmonella
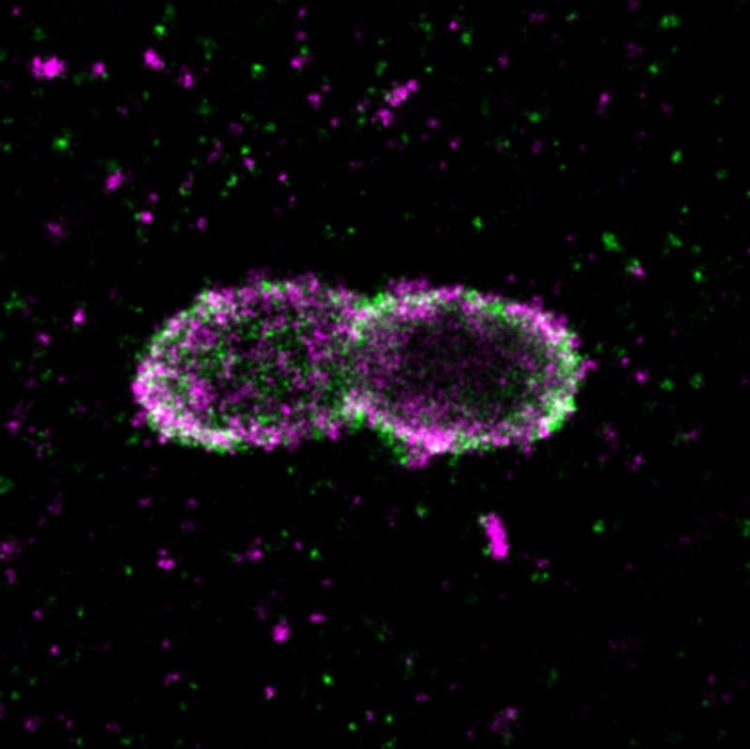
Salmonella within a human cell, surrounded by a coat of different ubiquitin chains. Purple represents linear ubiquitin chains, green all ubiquitin chains. Visualized by super-resolution microscopy. Mike Heilemann/Ivan Dikic
All bacteria have developed clever mechanisms for survival and propagation within host cells. Salmonella are a typical example: usually they hide in membrane-bound particles with only very few bacteria escaping to the cell’s interior. Those escapees are extremely dangerous as they proliferate and spread at enormous speed.
To stop such an invasion, cells have developed very effective defense strategies. An interdisciplinary team around Prof. Ivan Dikic (Institute of Biochemistry II) and Prof. Mike Heilemann (Institute of Physical and Theoretical Chemistry), both from Goethe University Frankfurt, now studied such a cellular defense mechanism by visualizing protein patterns at the near-molecular level.
Protein chains relay pro-inflammatory signals
Upon bacterial invasion, cells react fast: They flag escaped bacteria with a small protein called ubiquitin, which is known to regulate numerous cellular processes. The attached flags contain chains of differently linked ubiquitin molecules, resulting in a secret code, which has so far only partially been decoded. Similar to mobile transmission towers, these ubiquitin chains relay specific signals from the surface of the bacteria into the cell.
Employing super-resolution microscopy, the Frankfurt team now succeeded with visualizing different ubiquitin chains on the bacterial surface and analyzing their molecular organization in detail. They discovered that one chain type, so called linear chains, plays an essential role during a bacterial invasion.
Linear ubiquitin chains trigger degradation of bacteria and kick off an inflammatory signaling cascade which results in restricting bacterial proliferation. In addition, the researchers identified the enzyme Otulin as an important regulator capable of limiting this reaction – a very important notion considering the fact that excessive inflammation is one of the major causes of tissue damage following bacterial infection.
Signaling the cells’ need for pathogen defense is just one important role of ubiquitin. The small protein is also involved in development and progression of inflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases as well as of cancer. Until now, however, very little is known about how small errors in the ubiquitin system contribute to these serious human diseases, and how the system can be targeted pharmaceutically.
These new findings pave the way for many follow-up projects which may ultimately lead to novel therapeutic approaches. Very recently, Ivan Dikic obtained one of the prestigious ERC Advanced Grants of 2.5 M € in which he will investigate the role of ubiquitin in modulating the host-pathogen interaction in more detail.
The work of the Frankfurt team is an excellent example for interdisciplinary collaboration and was enabled by funding of several large research networks, e.g. the Cluster of Excellence Macromolecular Complexes, the CRC 1177 on selective autophagy and the LOEWE ubiquitin network. The results are now published in the latest online issue of Nature Microbiology, back-to-back with complementary insights generated by colleagues in Cambridge (UK).
Picture link: www.uni-frankfurt.de/66465906
Captions: 1. Salmonella within a human cell, surrounded by a coat of different ubiquitin chains. Purple represents linear ubiquitin chains, green all ubiquitin chains. Visualized by super-resolution microscopy (dSTORM). Copyright: Mike Heilemann/Ivan Dikic
2. One Salmonella bacterium within a human cell, surrounded by a coat of different ubiquitin chains. Purple represents linear ubiquitin chains, green all ubiquitin chains. Visualized by super-resolution microscopy (dSTORM). Copyright: Mike Heilemann/Ivan Dikic
3. One Salmonella bacterium within a human cell, surrounded by a coat of different ubiquitin chains. The coloured dots represent individual linear ubiquitin chains. Visualized by super-resolution microscopy (3D-dSTORM). Copyright: Mike Heilemann/Ivan Dikic
Publication: van Wijk SJ, Fricke F, Herhaus L, Gupta J, Hötte K, Pampaloni F, Grumati P, Kaulich M, Sou Y, Komatsu M, Greten F, Fulda S, Heilemann M, Dikic I. Linear ubiquitination of cytosolic Salmonella Typhimurium activates NF-κB and restricts bacterial proliferation. Nature Microbiology 2017, doi 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2017.66.
Information: Dr. Kerstin Koch, Institute of Biochemistry II, Faculty 16, University Hospital Frankfurt, Phone +49 (0)69 6301 84250, k.koch@em.uni-frankfurt.de.
Goethe University is a research-oriented university in the European financial centre Frankfurt The university was founded in 1914 through private funding, primarily from Jewish sponsors, and has since produced pioneering achievements in the areas of social sciences, sociology and economics, medicine, quantum physics, brain research, and labour law. It gained a unique level of autonomy on 1 January 2008 by returning to its historic roots as a “foundation university”. Today, it is among the top ten in external funding and among the top three largest universities in Germany, with three clusters of excellence in medicine, life sciences and the humanities. Together with the Technical University of Darmstadt and the University of Mainz, it acts as a partner of the inter-state strategic Rhine-Main University Alliance.
Current news about science, teaching, and society in GOETHE-UNI online (www.aktuelles.uni-frankfurt.de)
Publisher: The President of Goethe University
Editor: Dr. Anne Hardy, Press Information Officer, Phone: +49(0)69 798-12498, Fax +49(0)69 798-761 12531, hardy@pvw.uni-frankfurt.de
Internet: www.uni-frankfurt.de
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



