Bacteria Free Themselves with Molecular “Speargun”
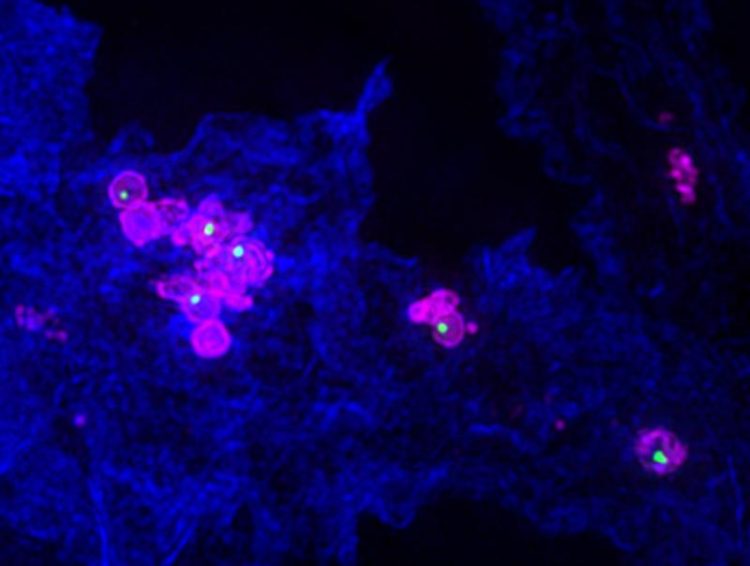
Macrophage infected with Francisella novicida (magenta) assembling a dynamic nano-speargun (green) University of Basel, Biozentrum
Tularemia is an infectious disease that mostly affects rabbits and rodents, but also humans can become infected. The cause of this serious disease is the bacterium Francisella tularensis. The infection biologists led by Prof. Marek Basler and Prof. Petr Broz, from the Biozentrum of the University of Basel, demonstrate on a Francisella subspecies which is harmless to man, how these bacteria escape from digestive vesicles in defense cells using a nano-speargun.
Tularemia: a serious infectious disease
This zoonotic disease can spread to humans mainly through parasites such as ticks and fleas or by airborne infection. Without medical treatment, the disease can be fatal. “The mortality rate can be as high as thirty percent,” explains Broz. “Inhaling as little as a dozen Francisella bacteria is sufficient to get infected.” Since the pathogen is highly contagious and can spread rapidly through the air it has been included in the arsenal of biological weapons.
Pathogen has its own “weapon”
The bacterium Francisella, however, has an efficient “weapon” of its own – the so-called type VI secretion system (T6SS) – which basically works like a spear gun. The bacterium uses this nano-machine to escape from their “prison” in the phagocytes. These defense cells “ingest” pathogens that invade the body, enclosing them in small vesicles and digest them completely. However, by using the T6SS, Francisella disrupts these digestive vesicles and escapes into the cytosol, an environment where it can rapidly replicate.
Molecular speargun to escape from “prison”
The two research groups have now investigated the assembly and function of the T6SS in Francisella. In their study they have shown that the pathogen recycles its weapon. “After firing the speargun, it is immediately disassembled into its individual components. The bacterium then uses these components again to assemble a new T6SS,” says Basler. “With this weapon, the bacteria puncture the vesicle membrane, in which they are enclosed, and deliver toxic proteins into the cytosol of the immune cell.”
These so far uncharacterized effectors then disrupt the vesicle. This enables the bacteria to escape from their “imprisonment” and prevent their digestion. If they lack these effector proteins, they have no chance of escape. The T6SS as well as the toxic proteins are important virulence factors, as they are crucial e for the bacterium’s success in an infection. Once the bacteria reach the cytosol, the fight is not yet over, as they need to successfully evade recognition and elimination by powerful innate immune responses.
Original source
Maj Brodmann, Roland F. Dreier, Petr Broz and Marek Basler
Francisella requires dynamic Type VI secretion system and ClpB to deliver effectors for phagosomal escape
Nature Communications (2017), doi: 10.1038/ncomms15853
Further information
Prof. Dr. Marek Basler, University of Basel, Biozentrum, Tel. +41 61 207 21 10, email: marek.basler@unibas.ch
Dr. Katrin Bühler, University of Basel, Biozentrum, Communications, Tel. +41 61 207 09 74, email: katrin.buehler@unibas.ch
https://www.unibas.ch/en/News-Events/News/Uni-Research/Bacteria-Free-Themselves-…
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

A ‘language’ for ML models to predict nanopore properties
A large number of 2D materials like graphene can have nanopores – small holes formed by missing atoms through which foreign substances can pass. The properties of these nanopores dictate many…

Clinically validated, wearable ultrasound patch
… for continuous blood pressure monitoring. A team of researchers at the University of California San Diego has developed a new and improved wearable ultrasound patch for continuous and noninvasive…

A new puzzle piece for string theory research
Dr. Ksenia Fedosova from the Cluster of Excellence Mathematics Münster, along with an international research team, has proven a conjecture in string theory that physicists had proposed regarding certain equations….



