Why a Diabetes Drug Could Help in Parkinson’s Disease
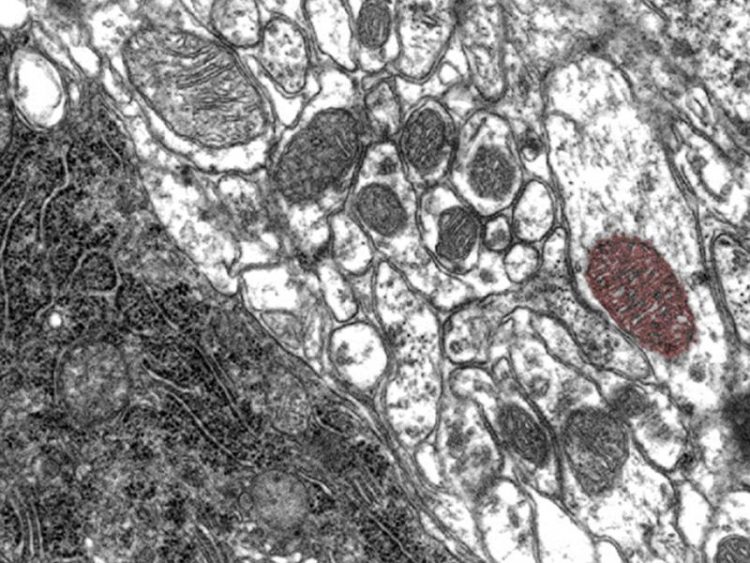
Cells imaged in an electron microscope. A mitochondrion of one cell is highlighted in red. Copyright: Hartwig Wolburg / Universität Tübingen
A diabetes drug might help in certain types of Parkinson’s disease, reports a team of German brain researchers headed by Dr. Julia Fitzgerald at the Hertie Institute for Clinical Brain Research, the University of Tübingen and the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases in Tübingen.
The neuroscientists identified a protein that plays an important role in the energy balance of cells. If the protein is missing, the energy balance is disturbed leading possibly to cell death and ultimately to the onset of the disease.
In Parkinson’s disease, nerve cells die off in a brain area responsible for movement control. Using cell cultures, the research team has now shown that the diabetes drug metformin acts on the energy budget, thereby protecting the cells. The study has been published in the current issue of the journal Brain.
“When studying cells from a patient suffering from Parkinson’s disease we saw that they lack an important protein which regulates the energy production,” explains Fitzgerald. As a result, the cells keep on producing energy in their mitochondria—the cells’ powerhouses—unchecked and less regulated.
Energy production comes at the cost of the generation of free oxygen radicals. The radicals damage the cell and lead to aging and, in the long term, sometimes to cell death. “The diabetes drug acts like a brake in this process. It slows down the uncontrolled generation of energy, thereby protecting the cells from the negative effects,” the researcher reports.
The study by the Tübingen neuroscientists provides another indication that diabetes drugs might have a positive influence on certain types of Parkinson’s disease. “Only recently, an Anglo-American research collaboration showed that another diabetes drug can reduce movement disorder symptoms in patients with Parkinson’s disease,” says Fitzgerald.
The new findings of Fitzgerald and her colleagues contribute to the development of personalized medicine which aims at treating the disease with interventions tailored to the underlying individual trigger factor in each patient. In Parkinson’s disease, both hereditary predisposition and environmental influences play a role in the development of the disease.
“Ultimately, the cause varies from person to person,” explains Fitzgerald. “In the long term, our study will be beneficial to patients suffering from faulty energy production in cells.” At present, there are no drugs available that may stop or slow down Parkinson’s disease, physicians may only treat symptoms. Worldwide, there are about 10 million people affected by the
disease.
Original Publication
Fitzgerald et al. (2017): Metformin reverses TRAP1 mutation-associated alterations in mitochondrial function in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 140(9), pp 2444–2459.
doi: 10.1093/brain/awx202
Contact
Dr. Julia Fitzgerald
Hertie Institute for Clinical Brain Research
University of Tübingen
Phone: +49 7071 29-87616
julia.fitzgerald[at]uni-tuebingen.de
https://www.hih-tuebingen.de Hertie Institute for Clinical Brain Research
https://www.uni-tuebingen.de University of Tübingen
https://www.dzne.de German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



