New Inhibitor Brings New Hope
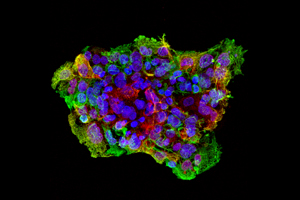
Breast cancer stem cell line 1 (BCSC1) from the newly established cell model. Here we can see the proteins keratin 5 in green and keratin 8 in red, with the nucleus in blue. Source: Maurer Lab
Scientists from the cluster of excellence BIOSS Centre for Biological Signalling Studies at the University of Freiburg and the Freiburg University Medical Center have shown that inhibiting the epigenetic regulator KDM4 might offer a potential novel treatment option for breast cancer patients.
They used a newly established cell model that enables scientists to isolate cancer stem cells directly from patient tumor. Using this special culture system, they were able to test potential new cancer drugs. One of these, a novel inhibitor of the epigenetic regulator KDM4, co-developed in the lab of Prof. Schüle, showed promising results. The researchers now published their work in the scientific journal Cancer Research.
Although the prognosis for breast cancer has been steadily improving in the last decades, patients with triple receptor-negative breast cancer form a subgroup who receive a considerably worse prognosis in most cases. Roughly 15 percent of all breast cancer patients have triple receptor-negative breast cancer, which lacks markers for a targeted therapy.
In the last few years, a bulk of data pointing to a small population of cells in tumors that maintain tumor growth, are particularly resistant to chemotherapy, are responsible for relapses, and develop metastases. These cells, named cancer stem-like cells, share many characteristics with the body’s normal stem cells. Due to their cancer-driving behavior, researchers have been focusing more and more on targeting these cells. However, there are currently only a few models available to study the biology of cancer stem cells.
Scientists from the University of Freiburg's new Center for Translational Cell Research have developed a model that allows scientists to isolate cancer stem cells from tumors obtained from breast cancer patients, thereby making biochemical and molecular analysis much more feasible.
Dr. Jochen Maurer and his research group were able to cultivate several cancer stem cell lines from triple receptor-negative breast cancer that are excellent representations of the original tumors they isolated from the patients.
In collaboration with Prof. Dr. Roland Schüle and his team at the Center of Clinical Research of the Freiburg University Medical Center, the scientists were able to test several epigenetic inhibitors that had been newly developed by Schüle and his team on the cancer stem cell model.
Epigenetics relates to the regulation of genes without involving changes in the DNA sequence and is regarded as one of the most important issues of the 21st century. It is believed that epigenetics play a huge role in the development and progression of cancer.
Schüle and his team have already conducted well-known studies on the epigenetic regulator LSD1. Now, they have discovered that an inhibitor of the epigenetic regulator KDM4 shows great promise in modulating breast cancer stem cell pathology.
They were able to block proliferation of several cancer stem cell lines. In addition, the KDM4 inhibitor induces a change of the molecular make-up of the cancer stem cells and drives them out of stemness. Finally, they were also able to reduce tumor growth in their first in vivo xenograft analysis.
Original Publication:
Metzger, E., Stepputtis, S.S., Strietz, J., Preca, B.T., Urban, S., Willmann, D., Allen, A., Zenk, F., Iovino, N., Bronsert, P., Proske, A., Follo, M., Boerries, M., Stickeler, E., Xu, J., Wallace, M.B., Stafford, J., Kanouni, T., Maurer, J., Schüle, R. (2017): KDM4 inhibition targets breast cancer stem-like cells. Cancer Research.
DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-1754
Caption:
Breast cancer stem cell line 1 (BCSC1) from the newly established cell model. Here we can see the proteins keratin 5 in green and keratin 8 in red, with the nucleus in blue.
Source: Maurer Lab
Contact:
Prof. Dr. Roland Schüle
Department of Urology and the Center of Clinical Research
Freiburg University Medical Center
BIOSS Centre for Biological Signalling Studies
Phone: +49 (0)761 / 203 – 63100
E-Mail: roland.schuele@uniklinik-freiburg.de
Dr. Jochen Maurer
Department of Visceral Surgery and Zentrum für Translationale Zellforschung
Freiburg University Medical Center
Tel.: 0761/270-63570
E-Mail: jochen.maurer@uniklinik-freiburg.de
https://www.pr.uni-freiburg.de/pm-en/2017/new-inhibitor-brings-new-hope
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni-freiburg.de/All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



