Violent helium reaction on white dwarf surface triggers supernova explosion
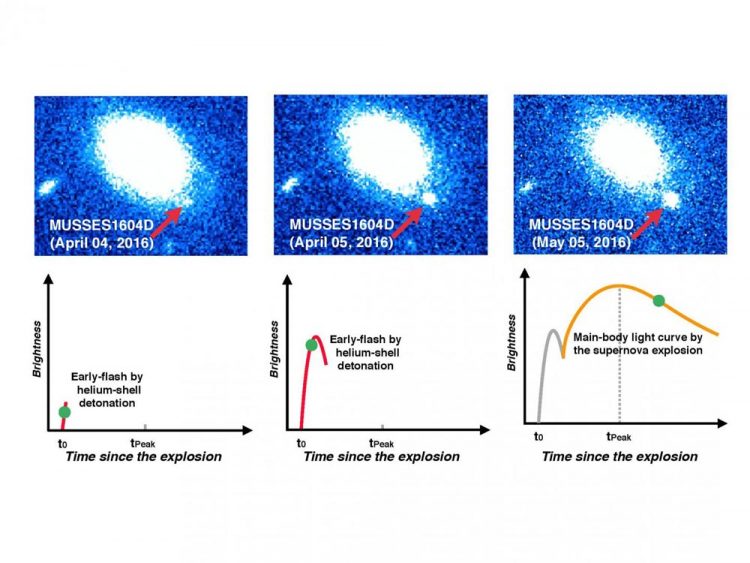
Upper panels show the first two-days observations of a peculiar type Ia supernova, MUSSES1604D, with Subaru/Hyper Suprime-Cam (left and middle) and follow-up observations with the Gemini-North telescope about one month after the first observation (right). Lower panels show the schematic light curves of MUSSES1604D (green circles denote the stages that the supernova is staying during observations). Credit: Institute of Astronomy, the University of Tokyo
A Type Ia supernova is a type of white dwarf star explosion that occurs in a binary star system where two stars are circling one another. Because these supernovae shine 5 billion times brighter than the Sun they are used in astronomy as a reference point when calculating distances of objects in space.
However, no one has been able to find solid evidence of what triggers these explosions. Moreover, these explosions only occur once every 100 years in any given galaxy, making them difficult to spot.
“Studying Type Ia supernovae is important because they are a valuable tool researchers use to measure the expansion of the universe. A more precise understanding of their history and behavior will help all researchers obtain more accurate results,” said author and University of Tokyo School of Science Professor Mamoru Doi.
A team of researchers including Senior Scientist Ken'ichi Nomoto, Professor Naoki Yasuda, and Project Assistant Professor Nao Suzuki from the Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe, and lead by University of Tokyo School of Science PhD candidate Ji-an Jiang and Professor Doi, Associate Professor Keichi Maeda at Kyoto University, and Dr. Masaomi Tanaka at the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, hypothesized Type Ia supernova could be the result of a white dwarf star consuming helium from a companion star.
The extra helium coating the star would trigger a violent burning reaction, which in turn would trigger the star to explode from within as a supernova.
To maximize the chances of finding a new or recent Type Ia supernova, the team used the Hyper Suprime-Cam camera on the Subaru Telescope, which can capture a large area of sky at once.
“Among 100 supernovae we discovered in a single night, we identified a Type Ia supernova that had exploded only within a day before our observation. Surprising, this supernova showed a bright flash in the first day, which we thought must be related to the nature of the explosion.
By comparing the observational data with what we calculated on how burning helium would affect brightness and color over time, we found both theory and observation were in good agreement. This is the first time anyone has found solid evidence supporting a theory,” said Maeda.
However, Nomoto says this does not mean they can explain everything about supernovae.
“In this study we found that a supernova was the result of the interaction between a white dwarf star and a companion star made of helium. But do we know whether this companion star was also a white dwarf star or a star much like our Sun? No we don't,” said Nomoto.
The team will continue to test their theory against other supernovae. Details of their study were published online in Nature on October 4.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



