Rice U. lab surprised by ultraflat magnets
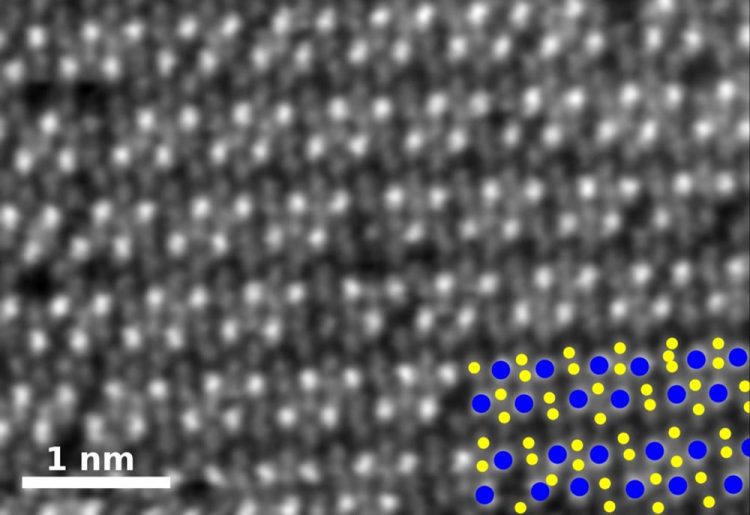
This is a high-angle annular dark-field image of pure rhenium diselenide. In the key at bottom right, rhenium atoms are blue and selenium atoms yellow. Credit: Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Substituting atoms in the process of making two-dimensional alloys not only allows them to be customized for applications but also can make them magnetic, according to Rice University scientists and their collaborators.
A new paper in Advanced Materials outlines how researchers at Rice, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, the University of Southern California (USC) and Kumamoto University in Japan used chemical vapor deposition (CVD) to make atom-thick sheets and, in the same step, tailor their properties by adding other elements through a process known as doping.
They discovered by surprise that they could also give the 2-D sheets magnetic properties.
The labs worked with transition metal dichalcogenides, alloys that combine a transition metal and chalcogen atoms into a single material. Transition metals are stable elements that fall in the middle of the periodic table. Chalcogens include sulfur, selenium and tellurium, also neighbors to each other in the table.
By adding a dopant element to the mix during CVD, the researchers showed it was possible to rearrange the atoms on the resulting 2-D crystal sheets. They demonstrated several different configurations and found they could replace some atoms outright with the dopant. These physical changes led to changes in the mechanical and electronic properties of the flat crystals, said co-author and Rice postdoctoral researcher Chandra Sekhar Tiwary.
The Rice lab of Pulickel Ajayan led the project to test theories by USC researchers who calculated that doping the materials would force a phase transition in the 2-D crystals. The Rice team confirmed the theory that adding rhenium in various amounts to molybdenum diselenide during growth would allow them to tailor its properties by changing its atomic structure. The magnetic signatures were a bonus.
“Usually, when you make a magnetic material, you start with magnetic elements like iron or cobalt,” said graduate student and co-lead author Amey Apte. “Rhenium, in bulk, is not a magnetic material, but it turns out it is in certain combinations at the atomic scale. It worked fantastically in this case.”
The researchers said the magnetic properties they discovered could make the 2-D alloys of interest to those who design spintronic devices.
###
Former Rice postdoctoral researcher Vidya Kochat is co-lead author of the paper. Co-authors are Rice graduate student Sandhya Susarla; postdoctoral researcher Jordan Hachtel and staff scientist Juan Carlos Idrobo of Oak Ridge; graduate student Hiroyuki Kumazoe of the University of Southern California and Kumamoto University; postdoctoral researcher Aravind Krishnamoorthy and professors Priya Vashishta, Rajiv Kalia and Aiichiro Nakano of the University of Southern California; and Fuyuki Shimojo of Kumamoto University. Ajayan is chair of Rice's Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering, the Benjamin M. and Mary Greenwood Anderson Professor in Engineering and a professor of chemistry.
The Computational Materials Science Program funded by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Basic Energy Sciences, supported the research.
Read the abstract at http://onlinelibrary.
This news release can be found online at http://news.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
Related materials:
Ajayan Research Group: http://ajayan.
Rice Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering: https:/
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,879 undergraduates and 2,861 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for quality of life and for lots of race/class interaction and No. 2 for happiest students by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read “What they're saying about Rice,” go to http://tinyurl.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



