Salmonella as a tumour medication
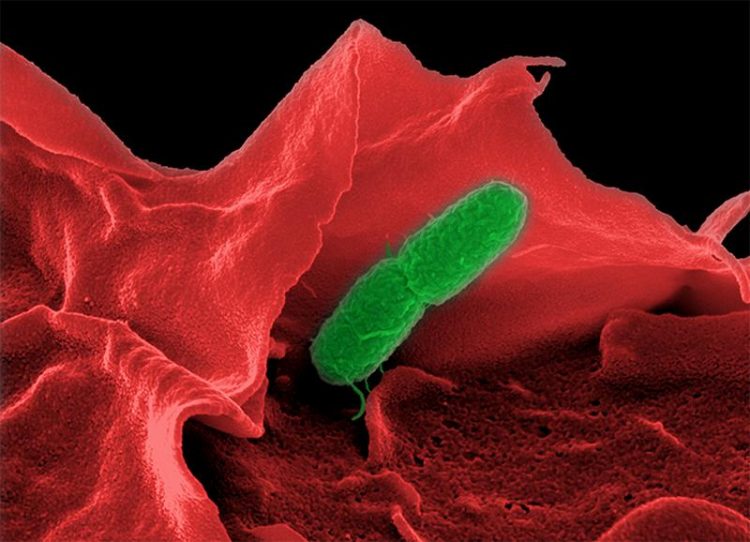
Electron microscopic image of Salmonella enterica (serovar Typhimurium). HZI/Manfred Rohde
Salmonellae are dangerous pathogens that enter the body via contaminated food and can cause severe infections. But these bacteria are also known to target tumours and to colonise them. Researchers are aiming to make use of this property for cancer therapy, but they are facing a dilemma:
Salmonella infections are life-threatening. Scientists from the Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research (HZI) in Braunschweig now undertook a successful step towards the clinical application. They developed a Salmonella strain that induces only a harmless infection, but activates the immune system strongly enough to fight the tumours. Their results were published in the journal OncoImmunology.
Cancer diseases are some of the most common causes of death throughout the world, and they are still gaining in significance as the average general population gets older. However, we still do not have a satisfactory therapy for many types of tumours. One extremely promising approach is to involve the immune system in the control of the tumour.
Scientists from the HZI use Salmonella enterica bacteria to activate the immune system to tumours and to trigger an inherent defence reaction. In cancer patients, salmonellae colonise tumour tissue specifically, but the infection can take a life-threatening course. “For this type of tumour therapy, a strain of Salmonella must not only trigger a strong defence reaction of the immune system, but it must also not be too aggressive such that we can keep it in check,” says Dr Sebastian Felgner, who is a scientist at the HZI.
The HZI researchers introduced genetic changes into the bacteria step-by-step and tried to find an optimal balance between safety and sufficient immune activation. “We changed numerous properties of the salmonellae, for example a component that eliminates the apparatus of motility and therefore restricts the mobility of the bacteria,” says Felgner.
In order to increase the visibility of the bacteria to the immune system, the scientists also addressed certain other molecules in the membrane – which is the outer shell – of the salmonellae. This is where so called lipopolysaccharides consisting of sugar chains and lipid chains are anchored. These molecules reside on the surface of the bacteria and are recognised by the immune system as being foreign.
To hide themselves upon infection, salmonellae have a number of enzymes that cleave lipid chains as soon as they enter the host. “We switched off those cleaving enzymes in our Salmonella strain. As a result, the lipid chains on the surface of the bacteria are preserved in the patients and are quite visible to the immune system,” says Felgner.
Following this scheme, the scientists introduced a number of other genetic modifications into their Salmonella strain and investigated the therapeutic effect in mice. In the course of this work, they successfully found a proper balance between attenuation of the bacteria and the intensity of the immune reaction, and even took another hurdle:
“One problem is that humans that have been exposed previously to the bacteria developed immunity against them and may possibly no longer respond to the therapeutic salmonellae,” says Dr Siegfried Weiß, the former head of the “Molecular Immunology” department of the HZI, who now works at the Hannover Medical School. “Therefore, a therapeutic strain must be able to overcome this inherent protection of the body, since salmonella infections are rather common, especially in countries with poor hygienic conditions where large parts of the population are immune.”
The numerous modifications introduced by the HZI researchers have now resulted in a Salmonella strain that mobilises the inherent defence even in mice that are immune to salmonellae. “Even tumours that used to be resistant to the strain are now eliminated by the immune system,” says Weiß.
The research is being done in close cooperation with the “Infection Biology of Salmonella” young investigator group of Prof Marc Erhardt, who recently joined the Humboldt University in Berlin. A patent for the newly developed Salmonella strain has been filed. “Our strain is safe and at the same time effective enough for tumour therapy,” says Sebastian Felgner. “The next step towards therapeutic application would be to test the strain in clinical studies in cooperation with industrial partners and to check its suitability for clinical application.”
Original publication:
Sebastian Felgner, Dino Kocijancic, Michael Frahm, Ulrike Heise, Manfred Rohde, Kurt Zimmermann, Christine Falk, Marc Erhardt, and Siegfried Weiss: Engineered Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium overcomes limitations of anti-bacterial immunity in bacteria-mediated tumor therapy. OncoImmunology, 2017, DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1382791
The press release and a picture are also available on our website: https://www.helmholtz-hzi.de/en/news_events/news/view/article/complete/salmonell…
Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research:
Scientists at the Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research (HZI) in Braunschweig, Germany, are engaged in the study of different mechanisms of infection and of the body’s response to infection. Helping to improve the scientific community’s understanding of a given bacterium’s or virus’ pathogenicity is key to developing effective new treatments and vaccines. http://www.helmholtz-hzi.de/en
Contact:
Susanne Thiele, Press Officer
susanne.thiele@helmholtz-hzi.de
Dr Andreas Fischer, Editor
andreas.fischer@helmholtz-hzi.de
Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research
Press and Communications
Inhoffenstr. 7
D-38124 Braunschweig
Germany
Phone: +49 531 6181-1404
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



