A new member of laser diode family: Electrically pumped organic semiconductor laser
Threshold and light amplification behaviors in organic semiconductor lasers. Credit: ©Science China Press
Low-cost organic semiconductor materials belong to four-level laser system that facilitates the realizing of population inversion. Organic lasers are small-sized, flexible, tunable and easily integrated laser sources for potential application in integrated photonic devices, visible light communication, sensors, medical and scientific research. While, for years, organic semiconductor lasing can only be observed under light excitation.
Because of large optical loss from device structure and complex excited state process, it is expected that an ultrahigh threshold current is required for the net gain. Electrically driven organic semiconductor lasers are facing great challenges as most organic materials have poor electrical conductivity.
In order to reduce the laser threshold, Prof. X. Liu's research team at Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has made a breakthrough in this field after years of research. Based on the principle of cavity quantum electrodynamics, planar microcavity of wavelength size can effectively control spontaneous emission and stimulated emission characteristics of organic semiconductors.
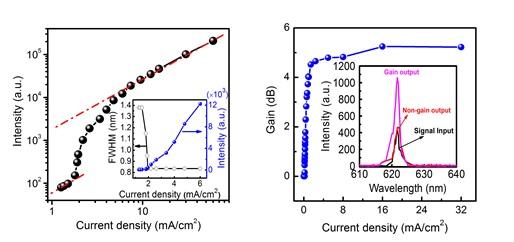
The research team has overcome the problem of high loss of electrode within cavity, designed and achieved a high quality factor microcavity organic laser device, and observed obvious gain amplification phenomenon at lower threshold current under quasi continuous operating.
The organic laser uses a small molecule doping system Alq:DCJTI as the gain medium, and the laser peak wavelength is located at 621.7 nm that remains unchanged with the increase of current. The threshold current density is about 1.8 mA/cm2, above which the spectral linewidth is narrowed to 0.835 nm.
The developed vertical cavity organic semiconductor optical amplifier shows a maximum optical gain of 5.25 dB under 16 mA/cm2 electrical pumping. Obtaining low laser threshold is an important step for the practical application of organic lasers, which will bring a room temperature continuous-wave lasing in the near future.
It indicates that optical loss in high-Q organic semiconductor microcavity is significantly reduced, and the underlying physics deserves further investigation.
###
See the article: Jie Lin, Yongsheng Hu, Ying Lv, Xiaoyang Guo, Xingyuan Liu, Light gain amplification in microcavity organic semiconductor laser diodes under electrical pumping, Science Bulletin, 2017, doi: https:/
http://www.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



