Throwing molecular wrench into gene control machine leads to 'melting away' of leukemia
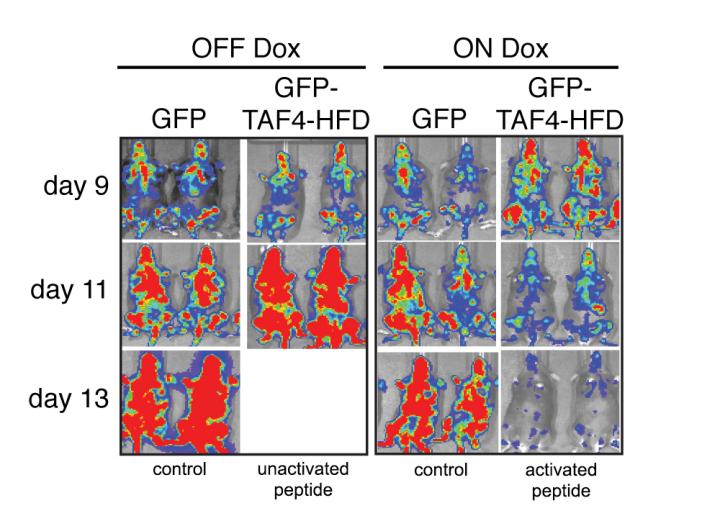
By inducing the expression of a small peptide in mouse models of human AML, CSHL researchers were able to prevent MYB, a major cancer enabler, from promoting cancer growth. Imaged 9, 11, and 13 days following introduction of the peptide, mice from the experiments show dramatic differences in outcome. In the left two columns, control (far left) and treated mice in which the peptide was not activated move from pervasive cancer (blue bioluminescence) to terminal (red). Some of the mice did not survive 13 days (blank panel). In contrast, the two right columns show control mice (poor outcomes) and treated mice with the peptide activated (far right). In the latter, in the far right column, one sees the cancer melt away, leaving the treated mice nearly cancer-free. Credit: Vakoc Lab, CSHL
In tests in mice, the newly discovered method has resulted in what the researchers describe as the “melting away” of aggressive blood cancers while at the same time having no harmful impact on the function of normal cells.
The new research by Associate Professor Christopher Vakoc and colleagues at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) is part of a broader effort in Vakoc's lab to fight the often fatal acute myeloid leukemia (AML) by disabling parts of the machinery in cells – called the transcriptional machinery — that determines when genes are switched on and off.
Central players in this machinery are proteins called transcription factors, thousands of which are active in regulating genes across our chromosomes. The question addressed in the new research, published today in Cancer Cell, was how to target one of the most troublesome transcription factors, called MYB. It's an oncogenic, or cancer-inducing, transcription factor that enables cells to blow through the stop signs that normally prevent out-of-control growth.
“MYB is a dream target in cancer research,” says Vakoc, “because it's involved in so many cancers; in leukemia it's special because we know from previous research that by targeting MYB you can get AML not just to stop growing but actually to regress.” Deactivating MYB in cancer has been a goal of many research labs..
Yali Xu, a Ph.D. student in the Vakoc lab leading the study, discovered how to selectively take MYB out of the picture in leukemia by throwing a molecular wrench into the mechanism that the transcription factor normally activates. First, the team discovered that MYB activates gene expression by docking at a giant gene-“co-activation” protein called TFIID (pronounced TF-two-D). Next, the they found a tiny weak spot on the massive protein. This Achilles' heel, called TAF12, is a small, nub-like projection. The team then tricked MYB into binding to short protein fragments, or peptides, that are shaped exactly like the place on TAF12 where MYB binds when it is promoting leukemia.
A major achievement in the study was generating this peptide, which acts like a decoy. Experiments in mice that model human AML showed that the peptide finds and binds MYB, preventing it from engaging the TFIID co-activator. This resulted in mouse leukemias shrinking in size by some 80% without causing harm to healthy cells.
While the peptide is not itself a drug, Vakoc says its action could be replicated by a drug. “It's a concept we're now discussing with the pharmaceutical industry. It is going to take lots of work before it can result in a medicine leukemia patients might take. But we're excited about this new approach, because MYB is such an important player in many cancers and until now has eluded efforts to selectively target it.”
###
Funding: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory NCI Cancer Center Support grant; Alex's Lemonade Stand Foundation; Forbeck Foundation; Pershing Square Sohn Cancer Research Alliance; V Foundation; Burroughs-Wellcome Fund Career Award; NIH/NCI; Leukemia & Lymphoma Society Scholar Award.
Citation: Xu, Y et al, “A TFIID-SAGA perturbation that targets MYB and suppresses acute myeloid leukemia.” Published online in Cancer Cell January 8, 2017.
About Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
Founded in 1890, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory has shaped contemporary biomedical research and education with programs in cancer, neuroscience, plant biology and quantitative biology. Home to eight Nobel Prize winners, the private, not-for-profit Laboratory employs 1,100 people including 600 scientists, students and technicians. The Meetings & Courses Program annually hosts more than 12,000 scientists. The Laboratory's education arm also includes an academic publishing house, a graduate school and the DNA Learning Center with programs for middle and high school students and teachers. For more information, visit http://www.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



