New filters could enable manufacturers to perform highly selective chemical separation
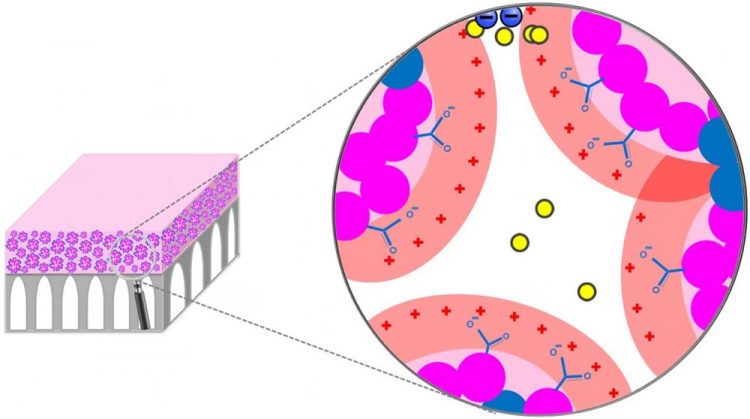
Membrane structure; the top layer (pink) shows selective layer morphology containing packed micelles. The spaces between the micelles form membrane nanopores with size of 1-3 nanometer Credit: Ilin Sadeghi, study co-author and Tufts University Ph.D. candidate
Tufts University scientists said the sophisticated membranes can separate organic compounds not only by size–as small as a molecule–but also by their electrostatic charge, meaning manufacturers could sort compounds by both size and type.
The membranes use a simple, scalable process in which a specialty polymer is dissolved in a solvent and coated onto a porous support. The polymer self-assembles to create approximately 1 nanometer size channels that mimic biological systems, such as ion channels, which control the passage of compounds through cell membranes with great effectiveness.
Corresponding-author Ayse Asatekin, Ph.D., a chemical and biological engineering professor in the Tufts School of Engineering, said the team's discovery responds to industry-wide calls for the development of more efficient solutions for separating chemicals, which accounts for 10 to 15 percent of global energy use, according to a report in Nature.
“Our study is promising because it is the first demonstration of a new way of making these selective membranes that are so important for chemical manufacturing,” she said. “Designing very selective membranes that can perform these complex separations could really boost energy efficiency and greatly reduce manufacturing waste.”
The newly designed membranes can:
- Allow neutral compounds to pass through 250 times faster than charged compounds of similar size;
- When charged and uncharged compounds are mixed, prevent the charged compound from passing through at all–its passage is averted because the neutral compound gets into the channels first and prevents the charge compound from entering; and
- Provide the ability to separate charged and uncharged compounds in various filtration systems.
Asatekin noted that the charge-based separation is enhanced when the solution contains a mixture of solutes, which indicates that the membrane structure successfully mimics how biological systems such as ion channels operate. This discovery has led the researchers to believe that this approach can be used to address other separations, and bring about selectivities above and beyond what can be attained using conventional membranes.
“This means we could potentially make filters that are capable of separations that cannot be achieved currently. Filters today usually are limited to separating big from small, and we want to be able to separate compounds that are the same size but different,” Asatekin said.
Asatekin noted some potential applications for this project include the purification of antibiotics, amino acids, antioxidants and other small molecule biologic compounds, and the separation of ionic liquids from sugar in biorefinery facilities. However, she said she believes this general approach may potentially be adapted further to different separations with further research.
Asatekin serves as the principal investigator of the Smart Polymers, Membranes, and Separations Laboratory at Tufts. The lab aims to develop the next generation of membranes by designing them from molecules up. The membranes rely on polymers that self-assemble, form nanostructures, and expose chemical functionalities that enable them to perform tasks normally not expected from membranes. They remove not only bacteria but also heavy metals, react to stimuli, and separate small molecules by chemical structure. Overall, the goal is to develop membranes that will help generate clean, safe water more efficiently and separate chemicals with lower energy use.
###
In addition to Asatekin, study authors include Ilin Sadeghi, Ph.D., a doctoral student, and Jacob Kronenberg, a senior undergraduate student, both of the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering in the School of Engineering at Tufts. This study was partially supported by the Tufts Collaborates Program and a National Science Foundation CAREER grant award (CBET-1553661).
Asatekin, A., Sadeghi, I., & Kronenberg, J., Selective transports through membranes with charged nanonchannels formed by scalable self-assembly of random copolymer micelles, ACS Nano. DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.7b07596. Published online Dec. 15, 2017; published in print Jan. 23, 2018.
About Tufts University
Tufts University, located on campuses in Boston, Medford/Somerville and Grafton, Massachusetts, and in Talloires, France, is recognized among the premier research universities in the United States. Tufts enjoys a global reputation for academic excellence and for the preparation of students as leaders in a wide range of professions. A growing number of innovative teaching and research initiatives span all Tufts campuses, and collaboration among the faculty and students in the undergraduate, graduate and professional programs across the university's schools is widely encouraged.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



