Demonstration of a single molecule piezoelectric effect
The converse piezoelectric effect in single heptahelicene-derived molecules. Credit: Pavel Jelínek / Institute of Physics of the CAS
Researchers from the Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry of the CAS (IOCB Prague), Institute of Physics of the CAS (IP CAS) and Palacký University Olomouc demonstrated for the first time a single molecule piezoelectric effect. The study published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society represents a breakthrough in understanding the electromechanical behavior of individual molecules and provides a new concept of the design of molecular motors, sensors and electricity generators at nanoscale.
The piezoelectric effect emerges in some materials in which the mechanical and electrical properties are coupled. Either the electric field can be generated if a mechanical stress is applied (direct piezoelectric effect) or, conversely, the mechanical deformation can arise if the electric field is applied (converse piezoelectric effect).
These effects have reached numerous practical applications in automotive, smartphone, computer, medical and military industries. In our everyday life, we meet the piezoelectric effect in smartphones, microphones or lighters, it is also widely employed in airbag systems, sonars or scanning microscopes. Possible applications of the piezoelectric effect to nanotechnology are currently under the spotlight and intensively studied. However, the single molecule piezoelectric effect, which is essential for envisioned electromechanical molecular devices, has so far remained elusive.
“In a close collaboration with physicists, it was proved for the first time that a strong converse piezoelectric effect can be observed at individual molecules of the heptahelicene derivative, which is a screw-like carbon molecule resembling a spring,” said Ivo Starý, the leader of the group of chemists at IOCB Prague preparing the compound.
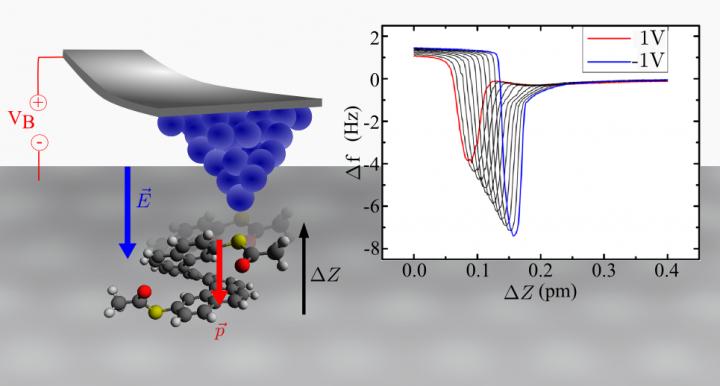
The effect was experimentally demonstrated by the group of physicists at IP CAS at individual molecules on a silver surface using scanning probe microscopy. The group leader Pavel Jelínek explains: “The magnitude of the piezoelectric constant calculated from the experimental data is significantly higher than that one of known piezoelectric polymers and is comparable to the magnitudes measured at some inorganic materials such as zinc oxide. Moreover, we explained the origin of the single molecule piezoelectric effect by employing quantum mechanics calculations.”
How does the converse piezoelectric effect work at nanoscale? The screw-like molecule endowed with an inner dipole stretches or squeezes itself depending on the strength and polarity of the outer electric field. It arises by applying a voltage bias between the silver pad and atomically sharp tip of the scanning microscope that resides over the studied molecule. As the change in a molecule height can be monitored with an ultimate accuracy, it is possible to see a molecule deformation induced by the electric field. Such a coupling of the mechanical movement of a molecule and the change in electric field, which is reciprocal by theory, represents an entry into the world of molecules doing mechanical work on one hand and molecular nanogenerators of electric energy on the other hand.
###
Article: O. Stetsovych, P. Mutombo, M. Švec, M. Šámal, J. Nejedlý, I. Císarová, H. Vázquez, M. Moro-Lagares, J. Berger, J. Vacek, I. G. Stará, I. Starý, P. Jelínek, Large Converse Piezoelectric Effect Measured on a Single Molecule on a Metallic Surface. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 940?946.
DOI: http://dx.
The Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry of the Czech Academy of Sciences / IOCB Prague is a leading scientific institution in the Czech Republic, recognized internationally. Its primary mission is basic research in the fields of chemical biology and medicinal chemistry, organic and material oriented chemistry, chemistry of natural compounds, biochemistry and molecular biology, physical chemistry, theoretical chemistry and analytical chemistry. The Institute has a long tradition and expertise in medicinal chemistry and drug development together with the pharma industry. Antivirals discovered by Antonín Holý and developed further by Gilead Sciences revolutionized the treatment of AIDS and hepatitis B and have significantly improved lives of millions of people around the globe.
Institute of Physics of the Czech Academy of Sciences / IP CAS is a public research institute, oriented on the fundamental and applied research in physics. IP is the largest institute of the Czech Academy of Sciences and its present research program comprises six branches of physics: particle physics, the physics of condensed matter, solid state physics, optics, plasma and laser physics. These research branches also define how the institute is structured into six major research divisions.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

A ‘language’ for ML models to predict nanopore properties
A large number of 2D materials like graphene can have nanopores – small holes formed by missing atoms through which foreign substances can pass. The properties of these nanopores dictate many…

Clinically validated, wearable ultrasound patch
… for continuous blood pressure monitoring. A team of researchers at the University of California San Diego has developed a new and improved wearable ultrasound patch for continuous and noninvasive…

A new puzzle piece for string theory research
Dr. Ksenia Fedosova from the Cluster of Excellence Mathematics Münster, along with an international research team, has proven a conjecture in string theory that physicists had proposed regarding certain equations….



