Newly designed molecule binds nitrogen
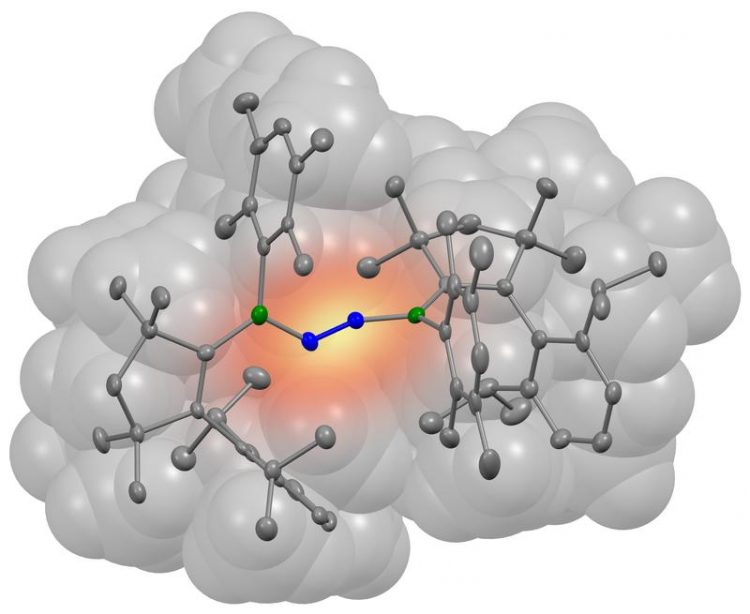
A nitrogen molecule (blue) has bonded with two borylene molecules (grey). The boron atoms involved in the bond are coloured green in the illustration. (Picture: Dr. Rian Dewhurst, JMU)
Whether wheat, millet or maize: They all need nitrogen to grow. Fertilisers therefore contain large amounts of nitrogenous compounds which are usually synthesised by converting nitrogen to ammonia in the industrial Haber-Bosch process, named after its inventors. This technology is credited with feeding up to half of the present world population.
Air consists of nearly 80 percent nitrogen (N2) which is, however, extremely unreactive, because the bond between the two nitrogen atoms is very stable. The Haber-Bosch process breaks this bond, converting nitrogen to ammonia (NH3) which can be taken up and used by plants. This step requires very high pressures and temperatures and is so energy intensive that it is estimated to consume 1% of the primary energy generated globally.
Bacteria lead the way
“So we were looking for a way to split nitrogen that is more energetically favourable,” explains Professor Holger Braunschweig from the Institute of Inorganic Chemistry at Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg (JMU) in Bavaria, Germany. Certain bacteria show that this actually works: They are capable of doing so at normal pressure and temperatures by using the nitrogenase enzyme which catalyses the reaction with the help of the transition metals iron and molybdenum.
“We have been unsuccessful in reproducing a kind of nitrogenase so far,” Braunschweig says. “So we started to look for an alternative: a molecule that is capable of catalysing the reaction and is not based on transition metals.”
His team has been studying specific boron-containing compounds, the so-called borylenes, for years. They are considered potential candidates for such a catalyst. But how exactly would the corresponding borylene molecule have to be structured for this purpose?
The candidates must be a good match for nitrogen
The iron and molybdenum in the nitrogenase are known to give away electrons to the nitrogen molecule, a process called reduction. This causes the bond between the two N atoms to break. However, this only works because the transition metals are a good match for the nitrogen molecule: Their orbitals, the space where the electrons passed during reduction can be found, overlap considerably with those of the nitrogen due to their spatial layout.
Based on quantum mechanical predictions, Dr. Marc-André Légaré from the Institute of Inorganic Chemistry designed a borylene with a similar orbital arrangement. The results of his investigations were then synthetically tested at the JMU institute.
And successfully so, as the borylene produced in this manner was capable of fixing nitrogen – and that at room temperature and normal air pressure. “For the first time, we were able to demonstrate that nonmetallic compounds are also capable of accomplishing this step,” Légaré emphasises.
Merely a first step
However, this does not mean that the Haber-Bosch process is about to be abolished. For one thing, it is not certain that the reduced nitrogen can be detached from the borylene without destroying it. However, this step is necessary to recycle the catalyst so that it is available to bond to the next nitrogen molecule subsequently.
“Whether this will ultimately yield a method that is more favourable energetically is still an open question,” says Professor Braunschweig. “It is only the very first step, albeit a major one, on the way to reaching the ultimate goal.”
The results of the study, which was carried out in collaboration with the research group of Professor Bernd Engels of the JMU Institute for Physical and Theoretical Chemistry, will be published in the renowned Science magazine.
Marc-André Légaré, Guillaume Bélanger-Chabot, Rian D. Dewhurst, Eileen Welz, Ivo Krummenacher, Bernd Engels and Holger Braunschweig: Nitrogen Fixation and Reduction at Boron; Science; 23. February 2018.
Contact
Prof. Dr. Holger Braunschweig, Chair of Inorganic Chemistry II, JMU, T +49 931 31-85260, h.braunschweig@uni-wuerzburg.de
http://www.braunschweiggroup.de/ Website of Braunschweig's team
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni-wuerzburg.deAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Nerve cells of blind mice retain their visual function
Nerve cells in the retina were analysed at TU Wien (Vienna) using microelectrodes. They show astonishingly stable behavior – good news for retina implants. The retina is often referred to…

State-wide center for quantum science
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology joins IQST as a new partner. The mission of IQST is to further our understanding of nature and develop innovative technologies based on quantum science by…

Newly designed nanomaterial
…shows promise as antimicrobial agent. Rice scientists develop nanocrystals that kill bacteria under visible light. Newly developed halide perovskite nanocrystals (HPNCs) show potential as antimicrobial agents that are stable, effective…



