Salk scientists find power switch for muscles
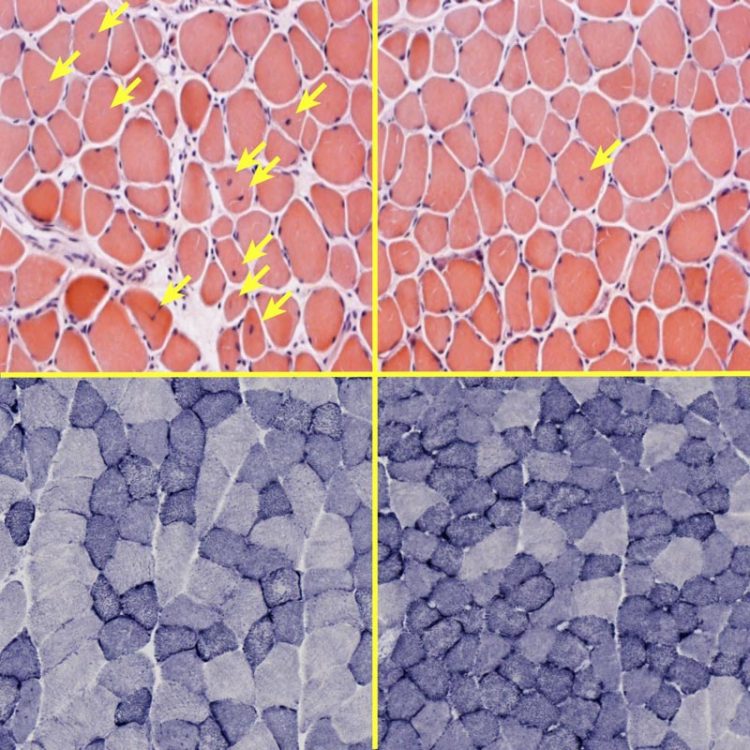
Top left: PGC1 deficiency leads to severe muscle damage, evidenced by numerous centralized nuclei (highlighted with arrows), which is likely due to impaired mitochondrial energy metabolism (bottom left: blue staining shows impaired mitochondrial activity). Such muscle damage and mitochondrial impairment is largely rescued by ERRγ overexpression (top and bottom right). Credit: Salk Institute
“ERRγ helps make endurance exercise possible,” says Ronald Evans, who is professor and director of the Gene Expression Laboratory and co-senior author on the paper. “It gears up the energy-creating cellular power plants known as mitochondria, creating more blood vessels to bring in oxygen, take away toxins and help repair damage associated with muscle use. This makes ERRγ a really interesting potential therapeutic target for conditions with weakened muscles.”
The story starts with the PGC1α and PGC1β proteins, which stimulate 20 other proteins associated with skeletal muscle energy and endurance exercise, including one from the Evans lab called ERRγ. In turn, ERRγ, a hormone receptor, acts to turn on genes. The Evans lab researchers wanted to precisely understand ERRγ's role in skeletal muscle energy production and how that impacts physical endurance.
To unravel this relationship, the Salk team studied mice without PGC1α/β. In some, they increased ERRγ selectively in skeletal muscle cells. This approach allowed them to measure how ERRγ and PGC1 act independently, as well as how they function in combination.
Losing PGC1 had a negative impact on muscle energy and endurance. However, boosting ERRγ restored function. The team found ERRγ is essential to energy production, activating genes that create more mitochondria. In other words, they found the power switch for skeletal muscles.
The lab also showed that increased ERRγ in PGC1-deficient mice boosted their exercise performance. By measuring voluntary wheel running, they found that increasing ERRγ produced a five-fold increase in time spent exercising compared to mice with no PGC1 and normal ERRγ levels.
“Now that we have detected this direct target (ERRγ) for exercise-induced changes,” says Weiwei Fan, a Salk research associate and the paper's first author, “we could potentially activate ERRγ and create the same changes that are being induced by exercise training.”
In addition to increasing the number of mitochondria in skeletal muscle cells, ERRγ also increased muscular blood flow.
“You have to get more blood supply in to get more energy and take away toxic metabolites,” says Michael Downes, a Salk senior scientist and co-senior author on the paper. “ERRγ boosts vascularization as well as mitochondria.”
But perhaps the most important finding is that ERRγ could be a significant therapeutic target in helping to repair damaged muscles.
“Mitochondria play such a central role in cells throughout the body, but particularly in muscle cells, which tend to require more energy,” says Evans. “We now know that, by increasing mitochondria energy output, ERRγ can actually rescue damaged muscle. If we can identify small molecules that specifically target ERRγ, we hope to help people with muscular dystrophy and other skeletal muscle conditions.”
###
Other authors included Nanhai He, Chun Shi Lin, Zong Wei, Nasun Hah, Wanda Waizenegger, Ming-Xiao He, Ruth T. Yu and Annette R. Atkins at Salk and Christopher Liddle at Sydney Medical School.
This study was funded by: the Office of Naval Research (ONR N00014-16-1-3159), National Institutes of Health (DK057978, HL105278, HL088093, ES010337 and CA014195), National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (P42ES010337), Department of the Navy, Office of Naval Research (N00014-16-1-3159), the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (512354 and 632886), The Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust (#2017PG-MED001), the Samuel Waxman Cancer Research Foundation, Ipsen/Biomeasure and the Glenn Foundation for Medical Research.
About the Salk Institute for Biological Studies:
Every cure has a starting point. The Salk Institute embodies Jonas Salk's mission to dare to make dreams into reality. Its internationally renowned and award-winning scientists explore the very foundations of life, seeking new understandings in neuroscience, genetics, immunology, plant biology and more. The Institute is an independent nonprofit organization and architectural landmark: small by choice, intimate by nature and fearless in the face of any challenge. Be it cancer or Alzheimer's, aging or diabetes, Salk is where cures begin. Learn more at: salk.edu.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



