Less is more? Gene switch for healthy aging found
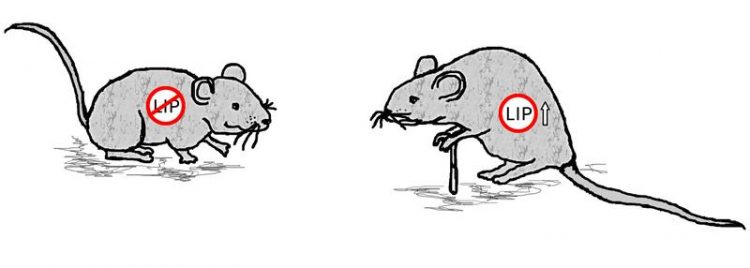
The C/EBPß-LIP gene regulator is involved in the aging process. If LIP is missing, the lifespan of mice increases and physical fitness is maintained during aging; without a calorie restriction. Figure: Kerstin Wagner / FLI
Aging is a major risk factor for physical frailty and the development of age-related diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, type II diabetes and Alzheimer's disease. Numerous studies have already shown that a calorie-restricted diet can significantly delay age-related conditions in several organisms like flies, worms, fish and mice, and that it even improves fitness at old age. But who wants to be on a lifetime diet?
Therefor it is important to clarify how a change in calorie intake affects health during aging and which genes play a role in this process. With this knowledge, it may be possible to find new therapeutic approaches that can delay aging and age-related diseases.
In an earlier project the researchers from the European Research Institute for the Biology of Ageing (ERIBA) in Groningen, Netherlands, and the Leibniz Institute on Aging (FLI) in Jena, Germany, have shown how the protein complex mTORC1 uses the gene switch C/EBPß to control the metabolism of mice: C/EBPß can occur in a short variant (LIP) and a long variant (LAP). A high activity of mTORC1 leads to an increased formation of the short (LIP) variant.
The activity of mTORC1 is regulated by food intake and can be significantly reduced by a calorie-restricted diet, which in turn inhibits the formation of LIP. If the production of the short LIP variant is permanently suppressed in a mouse strain developed by the researchers, the result is a healthier metabolism with reduced body weight and improved insulin sensitivity. These LIP-reduced knockin mice showed improved metabolic health, similar to mice under calorie restriction, although the LIP-reduced mice were not on such a diet.
Improving fitness in old age?
Based on these results, the researchers now examined whether the loss of LIP also results in an improvement in fitness in old age, similar to a diet. “The LIP-reduced mice are leaner at old age, they are able to cope better with changes in blood sugar levels, have a younger immune system, are significantly fitter and have a better motor coordination”, says Prof. Cornelis Calkhoven, former research group leader at the FLI and now at ERIBA, summarizing the most important results of the new study.
In addition, LIP-reduced mice developed less cancer later in life than control mice. “We show that the female mice lived about 20% longer without LIP than mice in the control group”, adds Dr. Christine Müller from ERIBA; an indication that the loss of LIP can extend lifespan.
Although male mice with no LIP didn’t show an increased lifespan, some of the age-related conditions were also less pronounced in the males. “If we find therapeutic ways to lower LIP levels in the body or to prohibit the effects of LIP, we may be able to delay the development of age-related diseases in the future”, emphasizes Dr. Müller, “without the constraints that are associated with a diet.”
Do only women benefit from such intervention?
“This is hard to say, as our results are based on a specific knockin mouse strain”, says Dr. Calkhoven about the research results. Other studies about calorie restriction also show differences between males and females that are not fully understood yet. “Therefore we have to continue our research in order to better understand the gender differences we have observed.” Nevertheless, this study shows that by reducing LIP or inhibiting its function a potentially new approach has been found to prevent the onset of age-related diseases or slow down the aging process.
Publication
Reduced expression of C/EBPβ-LIP extends health- and lifespan in mice. Müller C, Zidek LM, Ackermann T, de Jong T, Liu P, Kliche V, Zaini MA, Kortman G, Harkema L, Verbeek DS, Tuckermann JP, von Maltzahn J, de Bruin A, Guryev V, Wang ZQ, Calkhoven CF. eLife. 2018, Apr 30, 7. pii: e34985. doi: 10.7554/eLife.34985.
Contact
Dr. Kerstin Wagner
Press and Public Relations
Phone: 03641-656378
Email: presse@leibniz-fli.de
Background information
The Leibniz Institute on Aging – Fritz Lipmann Institute (FLI) – upon its inauguration in 2004 – was the first German research organization dedicated to research on the process of aging. More than 330 employees from over 30 nations explore the molecular mechanisms underlying aging processes and age-associated diseases. For more information, please visit http://www.leibniz-fli.de.
Dutch European Research Institute for the Biology of Ageing (ERIBA) was founded by the University Medical Center Groningen (UMCG) in 2013. ERIBA is an internationally orientated research institute focusing on fundamental biological problems related to aging and age-associated diseases. See http://eriba.umcg.nl for more information.
The Leibniz Association connects 93 independent research institutions that range in focus from the natural, engineering and environmental sciences via economics, spatial and social sciences to the humanities. Leibniz Institutes address issues of social, economic and ecological relevance. They conduct knowledge-driven and applied basic research, maintain scientific infrastructure and provide research-based services. The Leibniz Association identifies focus areas for knowledge transfer to policy-makers, academia, business and the public. Leibniz Institutes collaborate intensively with universities – in the form of “WissenschaftsCampi” (thematic partnerships between university and non-university research institutes), for example – as well as with industry and other partners at home and abroad. They are subject to an independent evaluation procedure that is unparalleled in its transparency. Due to the institutes’ importance for the country as a whole, they are funded jointly by the Federation and the Länder, employing some 19,100 individuals, including 9,900 researchers. The entire budget of all the institutes is approximately 1.9 billion EUR. See http://www.leibniz-association.eu for more information.
http://www.leibniz-fli.de – Website Leibniz Intitute on Aging – Fritz Lipmann Institute (FLI) Jena
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



