Tuberculosis: clinical trials on a newly developed drug initiated
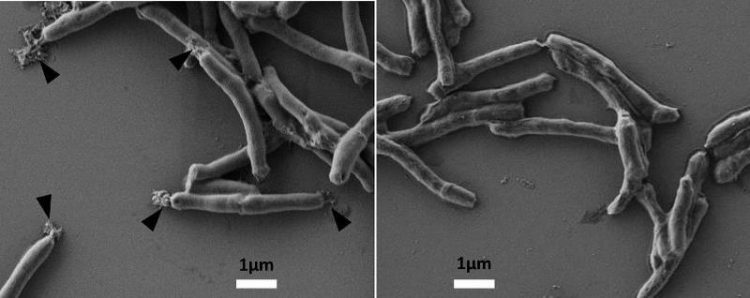
Tuberculosis bacteria: (left) treated with BTZ043, holes develop in the mycobacterial cell walls; (right) untreated Dr Andreas Wieser
The problem of antibiotic resistance has increased sharply over the last decades. Today, we face the challenge of having to manage a growing number of multidrug-resistant pathogens against which only a few antibiotics have remained effective.
In the case of tuberculosis, the situation is particularly difficult as the treatment regimen still includes several antibiotics which need to be taken simultaneously. Additionally, mycobacteria, which cause tuberculosis, have many mechanisms with which they protect themselves against specific effects of different antibiotics. Consequently, several new agents, ideally with different modes of action, are urgently needed to develop new treatment forms.
New site on mycobacteria targeted
BTZ043 is the first member of a newly discovered class of antibiotics and chemically belongs to the benzothiazinones. “The agent irreversibly binds to an enzyme that is needed for bacterial cell wall synthesis,” explains Dr Florian Kloß, Head of the Transfer Group Antiinfectives of InfectControl 2020 at the HKI.
“As the enzyme can then no longer function, holes develop in the mycobacterial cell walls and the cell contents drain out,” adds DZIF scientist Prof Michael Hoelscher, Director of the Department of Infectious Diseases and Tropical Medicine at the LMU Munich (also see image). “The agent targets tuberculosis bacteria highly selectively and consequently does not affect other bacteria.”
Clinical trial tests tolerance
Recruitment of the first trial subjects for clinical testing of BTZ043 can now be initiated, following the approval of the Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices (BfArM) and the Bavarian Chamber of Physicians’ Ethics Committee.
Led by Prof Hoelscher, up to 40 volunteers will receive the antibiotic at the trial centre of the company Nuvisan in Neu-Ulm. Hoelscher explains the procedure, “We want to ensure that the drug is absorbed by the body and is well-tolerated. To this end, a very low single dose will be administered, and subsequently this dose will gradually be increased for the next trial volunteers.” The aim of the trial is to reach the dose which showed good efficacy in animal models. This dose is far below the highest dose that the animals still tolerated well.
United against infections
A team of scientists and businessmen is involved in the development of this new tuberculosis drug. The agent, BTZ043, was discovered at the HKI in Jena. Since 2014, the drug has been developed further at the DZIF and InfectControl 2020 and other sites in a collaboration project between the Medical Center of the LMU Munich and the HKI.
The HKI is responsible for precise investigations of absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion as well as for developing analytical methods for detecting metabolites. As a funder, the LMU Munich’s Medical Center is responsible for preclinical and clinical development as well as for quality and safety of the drug. The substance will be produced at Hapila GmbH, a medium-size pharmaceutical company in Gera.
Financing the drug development costs of several million euros has been made possible though joint public and private funding. Particularly the two research alliances DZIF and InfectControl 2020 are involved in developing the active agent. They are being funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research.
Contact
Prof Michael Hoelscher
Department of Infectious Diseases and Tropical Medicine at the Medical Center of LMU Munich
T +49 89 2180 17613
E-mail: hoelscher@lrz.uni-muenchen.de
DZIF Press Office
Karola Neubert and Janna Schmidt
T +49 531 6181 1170/1154
E-mail: presse@dzif.de
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.dzif.deAll latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

Can lab-grown neurons exhibit plasticity?
“Neurons that fire together, wire together” describes the neural plasticity seen in human brains, but neurons grown in a dish don’t seem to follow these rules. Neurons that are cultured…

Unlocking the journey of gold through magmatic fluids
By studying sulphur in magmatic fluids at extreme pressures and temperatures, a UNIGE team is revolutionising our understanding of gold transport and ore deposit formation. When one tectonic plate sinks…

3D concrete printing method that captures carbon dioxide
Scientists at Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have developed a 3D concrete printing method that captures carbon, demonstrating a new pathway to reduce the environmental impact of the construction…



