Understanding anxiety – Neural circuit mechanisms of emotion identified
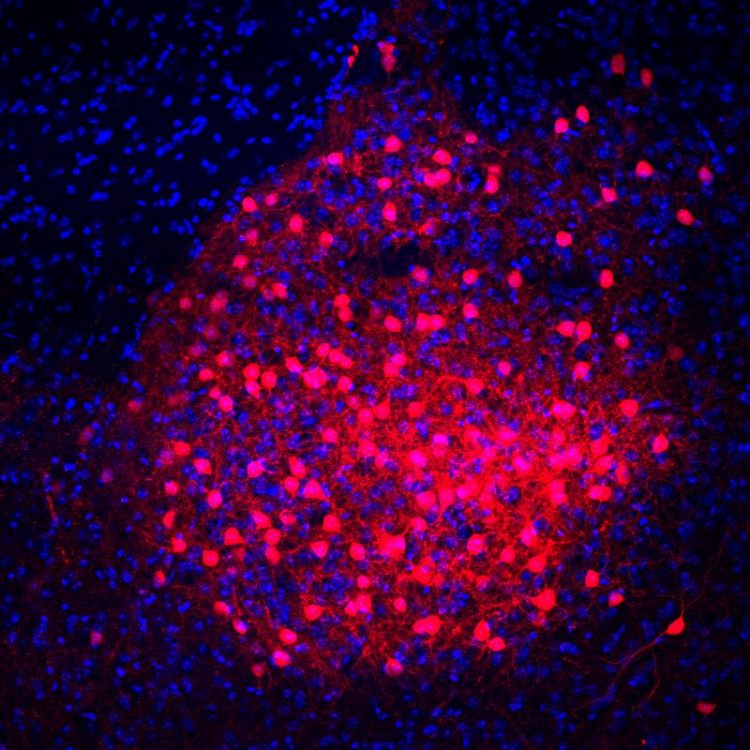
CRH neurons (red) in the amygdala MPI of Psychiatry
In a previous study, published in Science in 2011, Jan Deussing’s group revealed for the first time that corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) signaling in dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area (VTA) can suppress anxiety.
In their latest study, Deussing’s group has expanded on these findings, providing more mechanistic insights into the “anxiolytic” CRH circuit. Published in the prestigious journal Nature Neuroscience, the scientists describe how the circuit originates in the extended amygdala, in a population of GABAergic neurons that produce CRH.
They traced these neurons and saw that they project down to a region of the midbrain called the VTA, one of the main dopamine-producing areas of the brain. The VTA is known to play a key role in reward and addiction, but here the authors explain how CRH and dopamine interact in anxiety-related behavior.
The CRH-containing projection neurons of the extended amygdala target CRH receptors on dopaminergic VTA neurons. As a result, this circuit can regulate dopaminergic transmission and in turn, emotional behavior.
Lead author of the current study Nina Dedic explains the significance of the findings: “We know that CRH is a major driver of the stress response and that a hyperactive CRH system is implicated in neuropsychiatric pathologies such as mood and anxiety disorders. However, in this study, we could show that CRH does not always act as an aversive, stress-inducing neuropeptide. In fact, specific CRH circuits are required to maintain a positive affective state under normal, stress-free conditions.”
Deussing, research group leader and head of the study explains: “We were surprised to find that a subset of GABAergic CRH neurons in the extended amygdala carry dendritic spines and co-express the postsynaptic density protein, Camk2a. These characteristics are more commonly seen in excitatory, glutamatergic neurons.”
He continues: “Our work suggests that CRH neurons in the extended amygdala are more diverse than we had originally thought. There are locally projecting interneurons as well as spiny, GABAergic, long-range projection neurons.”
In addition to revealing how CRH interacts with dopamine to regulate anxiety, Deussing’s group hopes that these findings will help to unravel the complex stress circuits and networks of the brain.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



