A breakthrough in cardiac metabolic MR imaging
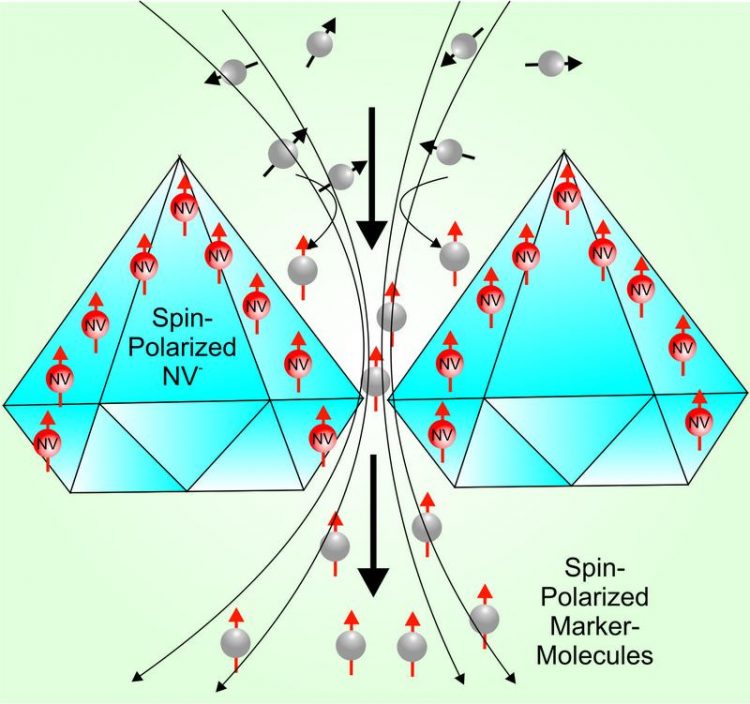
The technique used in MetaboliQs is based on the hyperpolarization of marker molecules like pyruvate used for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Foto: Dr. Christoph Nebel, Fraunhofer IAF
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) methods have been used widely in past decades as a safe, non-invasive and non-radioactive method of diagnosing CVDs. However, because of their limited sensitivity, even the most expensive MRI scanners (with the strongest magnets) cannot detect and visualize molecular and metabolic activity in the heart with sufficient sensitivity and specificity.
To this end, emerging hyperpolarized MRI techniques play a pivotal role as they allow increasing the sensitivity of MRI by up to five orders of magnitude. Unfortunately, the hyperpolarization process takes a very long time (90-180 minutes per procedure), it is extremely costly and cumbersome (>$2million initial cost, room size equipment) and requires temperatures colder than -270 degrees Celsius. The MetaboliQs project therefore aims to enable a new method for MRI by leveraging new advances in quantum physics.
Precision diagnostics and personalized treatment using quantum physics
The method, termed “Hyperpolarized MRI”, will allow imaging and visualization of key metabolic substrates in the heart and other organs (e.g., kidney, liver) via hyperpolarization of nuclear spins of substrates that are natural to the body and non-toxic. In this way, a number of important metabolic reactions can be tracked non-invasively.
This breakthrough technology will enable a previously unachievable, highly sensitive quantification of metabolic activity, paving the way for precision diagnostics and better personalized treatment of cardiovascular diseases. For example, it will become possible to distinguish patients who will most likely benefit from invasive or pharmacologic cardiac interventions from those who will need other medical treatment, and to accurately diagnose patients at the disease’s early stages.
The MetaboliQs project will leverage the transformative features of diamond nitrogen vacancies (NV), such as high quantum coherence and quantum control, to offer a breakthrough in Cardiac Hyperpolarized MRI: A low cost and high-throughput diamond polarizer that can be used with any MRI scanner and show results within minutes instead of hours required per procedure.
This unique utilization of quantum coherence is made possible by new technology to atomically engineer diamond material (quantum-grade diamond), including 12C isotopic purification, precise control of nitrogen defect concentration and nanofabrication of the diamond surface.
The MetaboliQs consortium, through its combination of leading research institutes and innovative companies, provides the end-to-end expertise required to reach the ambitious objectives of the project and develop breakthrough capabilities in hyperpolarized MRI for cardiovascular applications.
MetaboliQs brings together a world-class multidisciplinary consortium:
a) Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Solid State Physics in Freiburg, Germany, a leading diamond quantum technology research institute and frontrunner in quantum-grade diamond growth and fabrication, b) NVision Imaging Technologies GmbH, Germany, Silicon-Valley backed Quantum Tech Company and inventor of diamond-based polarization, c) Element Six (UK) Limited, a world leader in research and production of synthetic diamond with a track record in the quantum space, d) The Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HUJI), Israel, leading diamond quantum technologies research institute, e) Bruker BioSpin GmbH – market leader in preclinical MRI and NMR spectroscopy and two of the top technical universities in Europe with research groups in hyperpolarized and cardiovascular MRI:
f) ETH Zurich in Switzerland
g) and the Technical University of Munich, Germany.
The project MetaboliQs is part of the overall initiative “Quantum Flagship”, funded by the European Union. This initiative intends on placing Europe at the forefront of the second quantum revolution, which is now unfolding worldwide. It aims to bring disruptive quantum technologies to the scientific arena and to society in general by bringing forward new commercial opportunities addressing global challenges, providing strategic capabilities for security and seeding yet unimagined applications for the future. The Project MetaboliQs started in October 2018 and will continue until the end of 2021.
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement No 820374.
https://www.iaf.fraunhofer.de/en/offers/diamond-devices/metaboliqs.html (Further information about the project)
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

A ‘language’ for ML models to predict nanopore properties
A large number of 2D materials like graphene can have nanopores – small holes formed by missing atoms through which foreign substances can pass. The properties of these nanopores dictate many…

Clinically validated, wearable ultrasound patch
… for continuous blood pressure monitoring. A team of researchers at the University of California San Diego has developed a new and improved wearable ultrasound patch for continuous and noninvasive…

A new puzzle piece for string theory research
Dr. Ksenia Fedosova from the Cluster of Excellence Mathematics Münster, along with an international research team, has proven a conjecture in string theory that physicists had proposed regarding certain equations….



