Rutgers researchers advance stem cell therapy with biodegradable scaffold
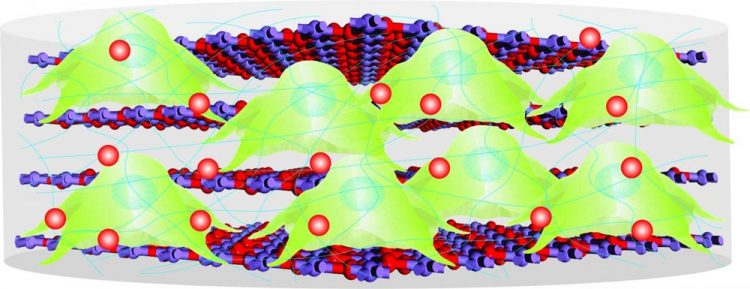
A biodegradable inorganic nano-scaffold, consisting of stem cells, proteins and drugs, for advanced stem cell therapy and drug delivery. Credit: KiBum Lee, Letao Yang and Sy-Tsong Dean Chueng.
Rutgers scientists have created a tiny, biodegradable scaffold to transplant stem cells and deliver drugs, which may help treat Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases, aging brain degeneration, spinal cord injuries and traumatic brain injuries.
Stem cell transplantation, which shows promise as a treatment for central nervous system diseases, has been hampered by low cell survival rates, incomplete differentiation of cells and limited growth of neural connections.
So, Rutgers scientists designed bio-scaffolds that mimic natural tissue and got good results in test tubes and mice, according to a study in Nature Communications. These nano-size scaffolds hold promise for advanced stem cell transplantation and neural tissue engineering. Stem cell therapy leads to stem cells becoming neurons and can restore neural circuits.
“It's been a major challenge to develop a reliable therapeutic method for treating central nervous system diseases and injuries,” said study senior author KiBum Lee, a professor in the Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology at Rutgers University-New Brunswick. “Our enhanced stem cell transplantation approach is an innovative potential solution.”
The researchers, in cooperation with neuroscientists and clinicians, plan to test the nano-scaffolds in larger animals and eventually move to clinical trials for treating spinal cord injury. The scaffold-based technology also shows promise for regenerative medicine.
###
The study included researchers from Rutgers and Kyung Hee University in South Korea.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05599-2All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



