Proposed engineering method could help make buildings and bridges safer
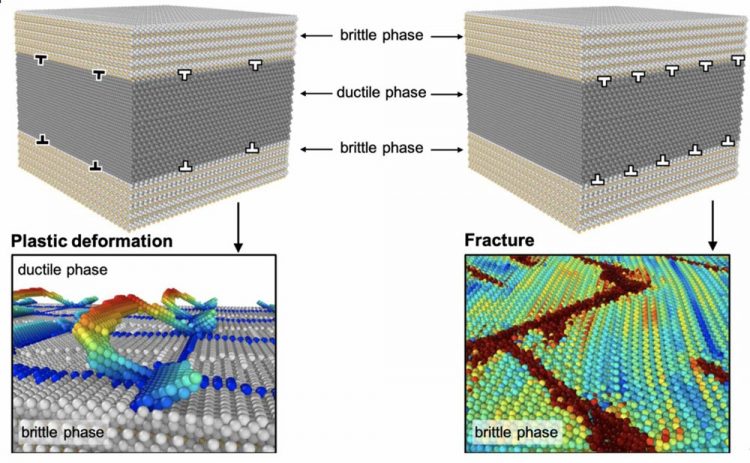
Interfacial-dislocation-controlled deformation and fracture in nanolayered composites. The spacing of the interfacial dislocations, which accommodate misfit strain between the ferrite and cementite phases, determines the phase stress and the interfacial dislocation network in the nanolayered-pearlite models. Various modes of initially activated inelastic-deformation are observed according to interfacial dislocation spacing because the phase stress and the interfacial dislocation network influence the resolved shear/normal stress and the critical resolved shear/normal stress for each inelastic-deformation mode, respectively. Hence, interfacial dislocation spacings can be a key parameter that controls the ductility of drawn pearlitic steels and leads us toward higher ductility of drawn pearlitic steels. Credit: Kanazawa University Usage Restrictions: The image may only be used with appropriate caption and credit.
Pearlitic steel, or pearlite, is one of the strongest materials in the world and can be made into thin and long wires. The strength of pearlite allows it to sustain very heavy weight, however what makes it special is its ability to stretch and contract without breaking (ductility).
Ductility is important for building bridges, as even if a material is strong enough to support heavy weight, it can break when subjected to stretching if it is not ductile enough.
This is why structures made of concrete can still collapse during violent earthquakes. Pearlite is used for suspension bridges to help them withstand strong shaking while supporting heavy weight.
Pearlite is made of alternating nanolayers of cementite and ferrite. The cementite helps make it strong, while the ferrite helps make it ductile. However, until now researchers did not know exactly how the two worked together to give pearlite its special quality, or better yet, how to control their working together to engineer an even better material.
Researchers at Kanazawa University have discovered that disruptions, or dislocations, in the arrangement of atoms along the interface between a cementite and a ferrite layer protect the cementite from fracturing under stretching or compression. Their study was published last month in the journal Acta Materialia.
“The spacing between dislocations on a cementite-ferrite interface determines how deformation travels through the nanolayers”, the authors say. “Manipulating the dislocation structure and the distance between dislocations can control the ductility of pearlite.”
The researchers used computer simulations to see how a pearlite wire would deform with dislocations of different orientations and different distances between them along the ferrite-cementite interface. They found that particular dislocation structures and distances could stop cracks from forming or spreading throughout the cementite layer.
“Increasing the ductility of pearlite means it can resist more shearing stress without breaking or tearing,” say the authors. This may lead to a new generation of materials for constructing buildings and bridges that can withstand stronger earthquakes.
The researchers believe manipulating dislocations consisting of entire clusters of atoms could be a general technique for enhancing not only ductility but other properties of materials to meet particular engineering and construction needs.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Architecture and Construction
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



