Combs of Light for Molecules
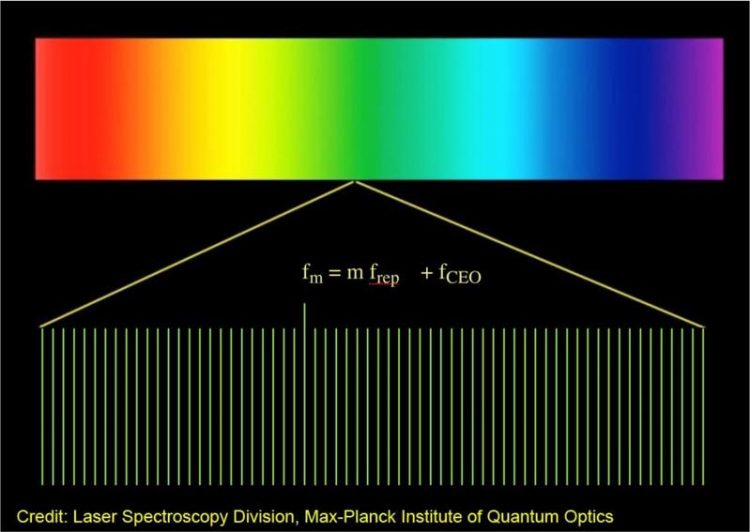
Figure 1: A frequency comb is a spectrum that spans a broad spectral bandwidth. It is composed of thousands or millions of phase-coherent sharp laser lines that are evenly spaced. MPQ
Atoms and molecules are the building blocks of matter. Spectroscopy can detect and identify a wide range of different compounds by their characteristic fingerprint-like absorption of radiation.
Applications range from basic studies of molecular structure and dynamics to industrial process control, environmental monitoring and medical diagnostics.
In recent years, powerful and potentially game-changing new tools for spectroscopy have emerged, based on mode-locked ultrafast lasers and their broad combs of evenly spaced sharp spectral lines.
A review article in Nature Photonics by Nathalie Picqué and Theodor W. Hänsch discusses developments and prospects in the emerging and quickly advancing field of atomic and molecular broadband spectroscopy with frequency combs.
A frequency comb (Figure 1) is a spectrum of phase-coherent sharp laser lines that are evenly spaced. Such combs based on femtosecond mode-locked lasers, as pioneered at the Max-Planck Institute of Quantum Optics in the 1990s, have revolutionized measurements of frequency and time.
In frequency metrology, a laser comb acts as a ruler in frequency space, that conveniently links microwave and optical frequencies, and/or measures a large separation between two optical frequencies. In the past decade, frequency combs have found new applications.
One of these is frequency comb spectroscopy: spectroscopy where the comb is used to directly excite or interrogate a sample. Molecular spectroscopy with frequency combs offers particularly intriguing opportunities, since complex spectra can be interrogated simultaneously by a large number of comb lines over a broad spectral range.
In a review article just published in the March-2019 issue of Nature Photonics, Nathalie Picqué and Theodor W. Hänsch, from the Laser Spectroscopy Division of the Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics and the Faculty of Physics of the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, present a summary of developments in the hot field of frequency comb spectroscopy and its emerging applications.
Frequency combs bring a set of new tools to spectroscopy in all phases of matter. The past decade has witnessed remarkable progress in laser frequency comb generators dedicated to broadband spectroscopy, especially in the molecular-fingerprint mid-infrared (2–20 μm) region and the ultraviolet range (<400 nm).
Such synthesizers harness modern tools of laser physics and nonlinear optics technology: mode-locked lasers, nonlinear frequency conversion, microresonators, electro-optic modulators, semi-conductor lasers etc. Existing spectrometers and spectrometric techniques have been adapted and improved to make the most of such sources, while entirely new comb-enabled approaches and instruments have been explored.
The new features enabled by frequency comb spectroscopy hold much promise for a vast number of applications ranging from fundamental physics to optical sensing. For instance, chip-scale frequency comb spectrometers may lead to integrated devices for chemical and biomedical sensing in real time.
Dr. Nathalie Picqué
Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics
Hans-Kopfermann-Str. 1, 85748 Garching, Germany
Phone: +49 89 32905 290
E-mail: nathalie.picque@mpq.mpg.de
N. Picqué, T.W. Hänsch
Frequency comb spectroscopy
Nature Photonics 13, 146-157 (2019)
doi: 10.1038/s41566-018-0347-5
SharedIt link: https://rdcu.be/bnRDN
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

A ‘language’ for ML models to predict nanopore properties
A large number of 2D materials like graphene can have nanopores – small holes formed by missing atoms through which foreign substances can pass. The properties of these nanopores dictate many…

Clinically validated, wearable ultrasound patch
… for continuous blood pressure monitoring. A team of researchers at the University of California San Diego has developed a new and improved wearable ultrasound patch for continuous and noninvasive…

A new puzzle piece for string theory research
Dr. Ksenia Fedosova from the Cluster of Excellence Mathematics Münster, along with an international research team, has proven a conjecture in string theory that physicists had proposed regarding certain equations….



