A thermo-sensor for magnetic bits
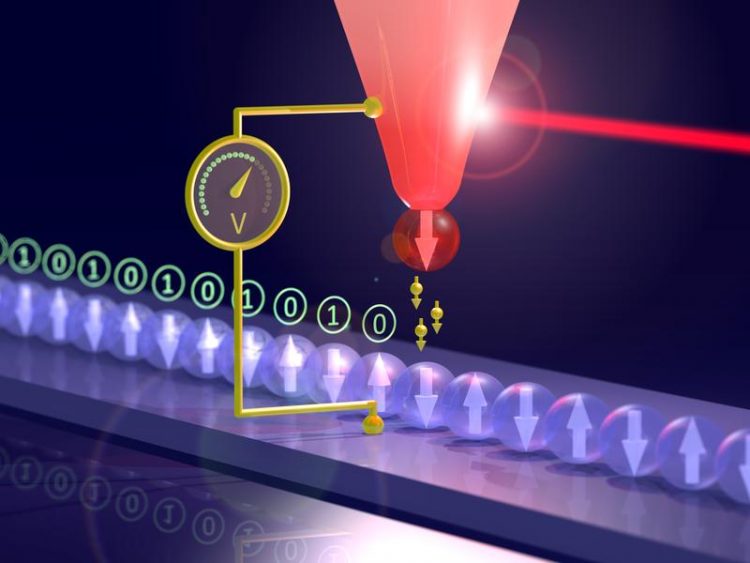
Schematic iillustration of the experimental setup: The tip of the scanning tunneling microscope is heated by a laser beam, resulting in a voltage that is used to read information from magnetic atoms. Stefan Krause (Univ. Hamburg)
Scientists of the Department of Physics at the University of Hamburg, Germany, detected the magnetic states of atoms on a surface using only heat. The respective study is published in the recent volume of the “Science” magazine.
A magnetic needle was heated by a laser beam and approached to within close proximity of a magnetic surface, with a gap of only a few atoms width. The temperature difference between the needle and the surface generates an electric voltage.
Scanning the needle across the surface, the scientists succeeded in showing that this thermovoltage depends on the magnetic orientation of the individual atom below the needle.
“With this concept we determined the surface magnetism with atomic accuracy without directly contacting or strongly interacting with the surface”, says Cody Friesen, the main author of the study. Conventional techniques need an electric current for this, which causes undesirable heating effects.
In contrast, the approach from Hamburg does not depend on a current. As a consequence for future applications, miniaturized magnetic sensors in integrated circuits may operate without a power supply and without generating waste heat.
Instead, process heat generated inside a device is directed towards the sensor, which thermally senses the magnetic orientation of an atom and translates it into digital information.
“Our investigations show that the process heat generated in integrated circuits can be used for very energy efficient computing”, says Dr. Stefan Krause, who supervises the project within the research group of Prof. Roland Wiesendanger.
Today, the ever increasing amount of data generation and the enhancement of processing speeds demand a constant miniaturization of devices, which leads to higher current densities and strong heat generation inside the devices. The new technique from Hamburg could make information technology more energy efficient and thus environmentally friendly.
Apart from ecological aspects, it would have meaningful implications for everyday life: Our smartphones would need less frequent recharging because of their reduced power consumption.
Dr. Stefan Krause
Department of Physics
University of Hamburg
Phone: +49 40 42838 7840
E-Mail: skrause@physnet.uni-hamburg.de
Prof. Dr. Roland Wiesendanger
Department of Physics
University of Hamburg
Phone: +49 40 42838 5244
E-Mail: wiesendanger@physnet.uni-hamburg.de
C. Friesen, H. Osterhage, J. Friedlein, A. Schlenhoff, R. Wiesendanger, and S. Krause,
Magneto-Seebeck tunneling on the atomic scale,
Science 363, 1065 (2019).
DOI: 10.1126/science.aat7234
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

A new puzzle piece for string theory research
Dr. Ksenia Fedosova from the Cluster of Excellence Mathematics Münster, along with an international research team, has proven a conjecture in string theory that physicists had proposed regarding certain equations….

Climate change can cause stress in herring larvae
The occurrence of multiple stressors undermines the acclimatisation strategies of juvenile herring: If larvae are exposed to several stress factors at the same time, their ability to respond to these…

Making high-yielding rice affordable and sustainable
Plant biologists show how two genes work together to trigger embryo formation in rice. Rice is a staple food crop for more than half the world’s population, but most farmers…



