OU engineers discover novel role of water in production of renewable fuels
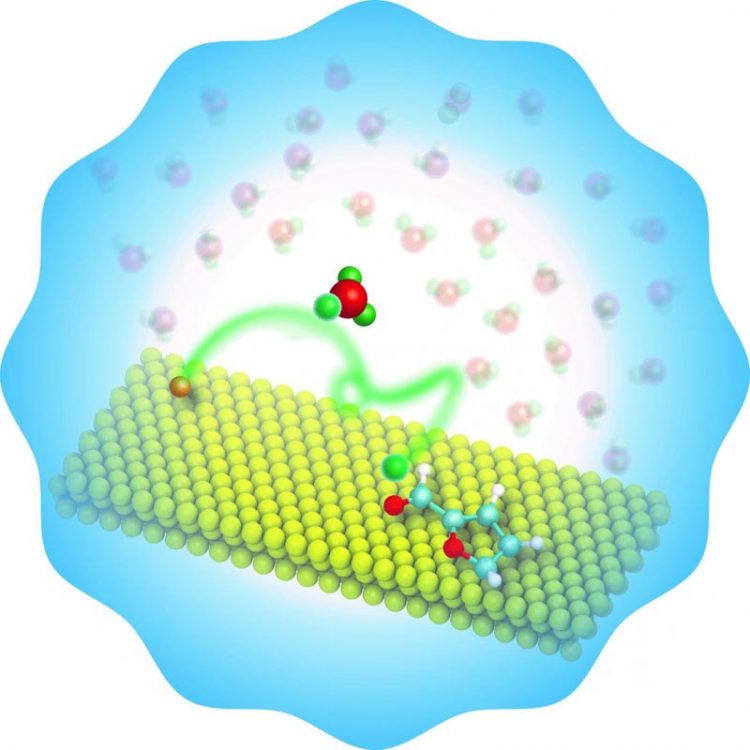
OU engineers have discovered a novel approach for the water-assisted upgrading of the renewable chemical, furfural, doubling or tripling the rate of conversion. Credit: University of Oklahoma
“Energy and water are interconnected in the production of renewable fuels. On the one hand, energy is needed to extract, purify and distribute water. On the other hand, water is useful in producing energy,” said Daniel Resasco, professor in the School of Chemical, Biological and Materials Engineering, Gallogly College of Engineering.
“It is known that water plays an important role as an environmentally-friendly solvent, replacing organic solvents. The novelty is that it can accelerate the rate of hydrogenation.”
In the chemical production of energy in conventional refining, the presence of water in the reactors is undesirable. Normally, when water is present in a reacting system where a catalytic reaction is taking place, it typically absorbs where the reaction should occur, which inhibits the rate of conversion.
“A group of chemical engineering graduate and undergraduate students participated in the discovery of water as a participant in the catalytic conversion of furfural without inhibiting the reaction and leading to a great rate enhancement in the process,” said Bin Wang, assistant professor in the School of Chemical, Biological and Materials Engineering, Gallogly College of Engineering.
Furfural is a biomass-derived compound that is considered a valuable platform for production of fuels and chemicals. An important strategy is to hydrogenate the molecule so it can be used in the chemical industry later. The group has shown that when the molecule contains an oxygenated group, hydrogenation occurs from the liquid phase instead of the catalyst surface.
In the absence of water, all steps in the reaction occur on the catalyst surface. In the presence of water as a solvent, the hydrogen can be 'shuttled' through the water molecule in a higher rate for the reaction. This latter path requires a lower energy barrier to take place and is faster. An article describing this unique mechanism has been published in Nature Catalysis.
###
The OU Catalysis Group received a U.S. Department of Energy grant in the amount of $650,000 to further explore the role of water in upgrading renewable fuels in the chemical production of energy.
For more information, contact OU Professor Resasco at resasco@ou.edu or OU Professor Wang at wang_cbme@ou.edu.
Media Contact
More Information:
https://bit.ly/2FNWnsZAll latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



