Energy-saving new LED phosphor
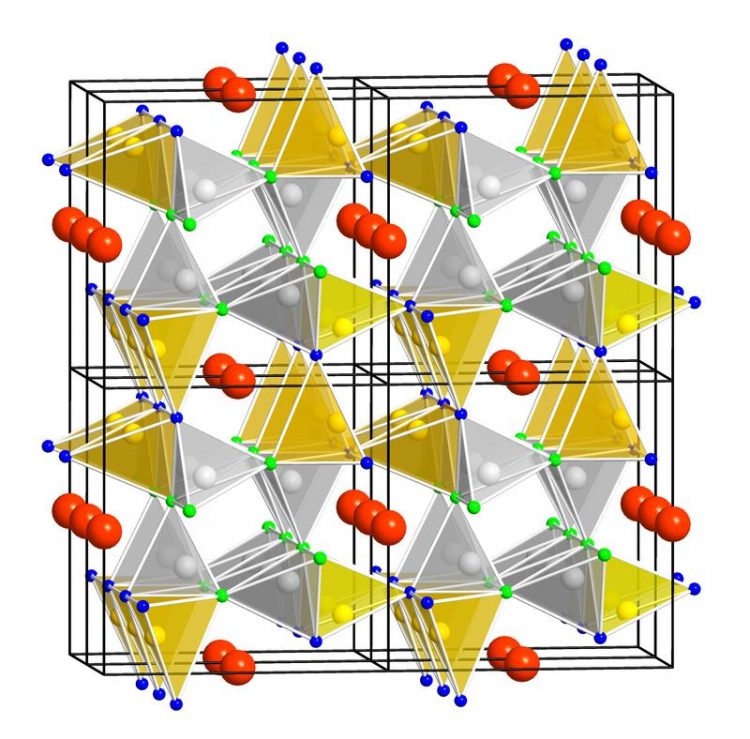
The crystal structure of the SALON phosphor is the reason for its excellent luminescence properties. Uni Innsbruck
Light emitting diodes or LEDs are only able to produce light of a certain colour. However, white light can be created using different colour mixing processes.
“In a white LED, red and yellow-green phosphors are excited by the light from a blue diode. The particles emit light in the red and green range, and in combination with the blue light they produce white light,” describes Hubert Huppertz from the Department of General, Inorganic and Theoretical Chemistry at the University of Innsbruck, Austria.
He and his team are working on improving the red and green phosphors. In cooperation with OSRAM Opto Semiconductors, his team has now succeeded in synthesizing a new red phosphor that has excellent luminescence properties and can make LED lighting significantly more energy-efficient.
Color shift improves luminous efficacy
The powerful red phosphor Sr[Li2Al2O2N2]:Eu2+, named SALON by the researchers, meets all the requirements for the optical properties of a phosphor. The development goes back to research carried out by Hubert Huppertz at the University of Bayreuth.
As part of his doctoral thesis, he developed nitrides doped with europium that are fluorescent. These were then further optimised by the working group in Munich and are now widely used. These red phosphors are partly responsible for the fact that LEDs no longer only glow cold white, but also warm white. Interestingly, the human eye reacts most sensitively to the colour green.
In the blue and red areas, the eye is less sensitive. Although these phosphors emit red light in the visible range, a large part of the energy goes into the infrared range, which the human eye does not perceive. The fluorescent material developed in Innsbruck has now succeeded in slightly shifting the light emission from red towards blue.
“Since initially only a few very small particles were available in a very inhomogeneous sample, it was difficult to optimise the synthesis,” said doctoral student Gregor Hoerder.
The breakthrough came when the researchers were able to isolate a single-crystal from one of the most promising synthesis products and thus determine the structure of the new material. “The substance is synthesised in such a way that it emits more orange than red,” says Hubert Huppertz. “With SALON we have less energy loss, it emits exactly in the red range we can see.”
OSRAM Opto Semiconductors, a strong industrial partner, the Fraunhofer Institute for Microstructures of Materials and Systems IMWS in Halle and Dirk Johrendt's research group at the Ludwig Maximilian University in Munich were also involved in further characterizing the new material. The development has already been registered for patent.
Univ.-Prof. Dr. Hubert Huppertz
Department of General, Inorganic and Theoretical Chemistry
University of Innsbruck
phone: +43 512 507 57000
email: hubert.huppertz@uibk.ac.at
web: http://www-c724.uibk.ac.at/aac/
Sr[Li2Al2O2N2]:Eu2+— A high performance red phosphor to brighten the future. Gregor J. Hoerder, Markus Seibald, Dominik Baumann, Thorsten Schröder, Simon Peschke, Philipp C. Schmid, Tobias Tyborski, Philipp Pust, Ion Stoll, Michael Bergler, Christian Patzig, Stephan Reißaus, Michael Krause, Lutz Berthold, Thomas Höche, Dirk Johrendt & Hubert Huppertz. Nature Communications 10, 1824 (2019) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09632-w
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uibk.ac.atAll latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

A ‘language’ for ML models to predict nanopore properties
A large number of 2D materials like graphene can have nanopores – small holes formed by missing atoms through which foreign substances can pass. The properties of these nanopores dictate many…

Clinically validated, wearable ultrasound patch
… for continuous blood pressure monitoring. A team of researchers at the University of California San Diego has developed a new and improved wearable ultrasound patch for continuous and noninvasive…

A new puzzle piece for string theory research
Dr. Ksenia Fedosova from the Cluster of Excellence Mathematics Münster, along with an international research team, has proven a conjecture in string theory that physicists had proposed regarding certain equations….



