New unprinting method can help recycle paper and curb environmental costs
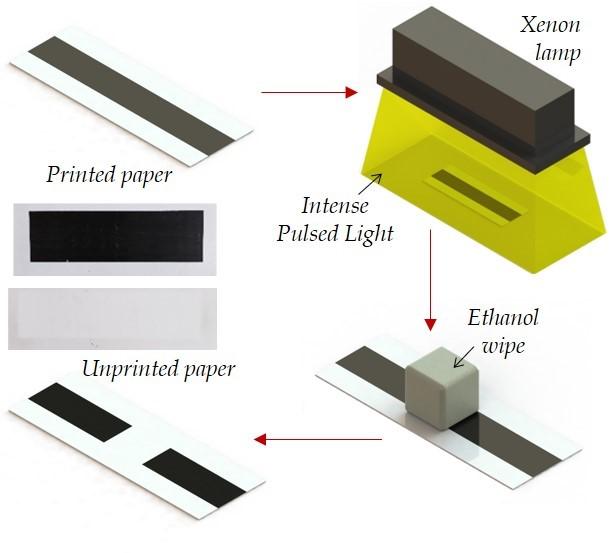
A new way to unprint paper using intense pulsed light from a xenon lamp. Credit: Rajiv Malhotra/Rutgers University-New Brunswick
Imagine if your printer had an “unprint” button that used pulses of light to remove toner, curbing environmental impacts compared with conventional paper recycling.
A Rutgers-led team has created a new way to unprint paper that, unlike laser-based methods, can work with the standard, coated paper used in home and office printers.
The new method uses pulses of light from a xenon lamp, and can erase black, blue, red and green toners without damaging the paper, according to a study in the Journal of Cleaner Production.
“Our method makes it possible to unprint and then reprint on the same paper at least five times, which is typically as many times paper can be reused with conventional recycling. By eliminating the steps involved in conventional recycling, our unprinting method could reduce energy costs, pollution and greenhouse gas emissions,” said study coauthor Rajiv Malhotra, an assistant professor in the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering in the School of Engineering at Rutgers University-New Brunswick.
Conventional recycling of coated paper is a major contributor to climate change emissions, chemical pollution and energy use, according to the study. Extending the life of paper while avoiding these recycling steps would yield significant environmental benefits.
The engineers' next steps are to further refine the method by testing additional toner colors on a wider range of paper types. Unprinting can be done with simple equipment and a wipe with a very small amount of benign alcohol, and the engineers are working to integrate unprinting with typical office and home printers.
###
The study's lead author is Michael Dexter, a former Rutgers engineering doctoral student. Former undergraduate engineering student Keri Rickman contributed to the study, along with researchers at Oregon State University.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Studies and Analyses
innovations-report maintains a wealth of in-depth studies and analyses from a variety of subject areas including business and finance, medicine and pharmacology, ecology and the environment, energy, communications and media, transportation, work, family and leisure.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



