Sea level rise: West Antarctic ice collapse may be prevented by snowing ocean water onto it
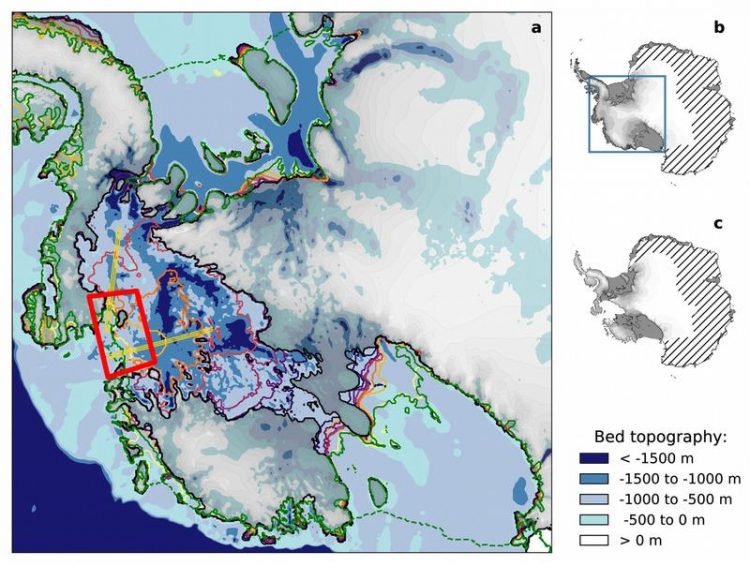
The red frame marks the area where the snowing would take place. Levermann et al 2019
A team of researchers from the Potsdam Institute is now scrutinising a daring way of stabilising the ice sheet: Generating trillions of tons of additional snowfall by pumping ocean water onto the glaciers and distributing it with snow canons.
This would mean unprecedented engineering efforts and a substantial environmental hazard in one of the world’s last pristine regions – to prevent long-term sea level rise for some of the world’s most densely populated areas along coastlines from the US to China.
“The fundamental trade-off is whether we as humanity want to sacrifice Antarctica to safe the currently inhabited coastal regions and the cultural heritage that we have built and are building on our shores. It is about global metropolises, from New York to Shanghai, which in the long term will be below sea level if nothing is done“ explains Anders Levermann, physicist at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) and Columbia University and one of the authors of the study.
“The West Antarctic Ice Sheet is one of the tipping elements in our climate system. Ice loss is accelerating and might not stop until the West Antarctic ice sheet is practically gone.”
Unprecedented measures to stabilise the ice sheet
Warm ocean currents have reached the Amundsen Sea Sector of West Antarctica – a region comprising several glaciers that are prone to instability due to their topographic configuration. Underwater melting of these glaciers triggered their speed-up and retreat.
This is already now responsible for the largest ice loss from the continent and provides an accelerating contribution to global sea level rise. In their study, the researchers employ computer simulations to project the dynamic ice loss into the future.
They confirm earlier studies suggesting that even strong reduction of greenhouse gas emissions may not prevent the collapse of the West Antarctic ice sheet.
“So we investigated what could stop a potential collapse in our simulations and increased the snowfall in the destabilised region far beyond observations,” says PIK co-author Johannes Feldmann.
“In fact, we find that an awful lot of snow can indeed push the ice sheet back towards a stable regime and stop the instability. In practice, this could be realized by an enormous redisposition of water masses – pumped out of the ocean and snowed onto the ice sheet at a rate of several hundred billion tons per year over a few decades.”
A tremendous trade-off between hazards and hopes
“We are fully aware of the disruptive character such an intervention would have,” adds Feldmann. Uplifting, desalinating and heating the ocean water as well as powering the snow canons would require an amount of electric power in the order of several ten thousand high-end wind turbines. “Putting up such a wind farm and the further infrastructure in the Amundsen Sea and the massive extraction of ocean water itself would essentially mean losing a unique natural reserve.
Further, the harsh Antarctic climate makes the technical challenges difficult to anticipate and hard to handle while the potential hazardous impacts to the region are likely to be devastating.” Thus the risks and costs of such an unprecedented endeavour must be weighted very carefully against its potential benefits.
“Also, our study does not consider future man-made global warming. Hence this gigantic endeavour only makes sense if the Paris Climate Agreement is kept and carbon emissions are reduced fast and unequivocally.”
“The apparent absurdity of the endeavour to let it snow in Antarctica to stop an ice instability reflects the breath-taking dimension of the sea-level problem,” concludes Levermann.
“Yet as scientists we feel it is our duty to inform society about each and every potential option to counter the problems ahead. As unbelievable as it might seem: In order to prevent an unprecedented risk, humankind might have to make an unprecedented effort, too.”
Article: Johannes Feldmann, Anders Levermann, Matthias Mengel (2019): Stabilizing the West Antarctic Ice Sheet by surface mass deposition. Science Advances [DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aaw4132]
Weblink to the article once it is published: https://www.doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaw4132
Previous related research: Anders Levermann, Johannes Feldmann (2019): Scaling of instability timescales of Antarctic outlet glaciers based on one-dimensional similitude analysis. The Cryosphere [DOI:10.5194/tc-2018-252] https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-2018-252
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.pik-potsdam.deAll latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

A ‘language’ for ML models to predict nanopore properties
A large number of 2D materials like graphene can have nanopores – small holes formed by missing atoms through which foreign substances can pass. The properties of these nanopores dictate many…

Clinically validated, wearable ultrasound patch
… for continuous blood pressure monitoring. A team of researchers at the University of California San Diego has developed a new and improved wearable ultrasound patch for continuous and noninvasive…

A new puzzle piece for string theory research
Dr. Ksenia Fedosova from the Cluster of Excellence Mathematics Münster, along with an international research team, has proven a conjecture in string theory that physicists had proposed regarding certain equations….



