'Resonance' raman spectroscopy with 1-nm resolution
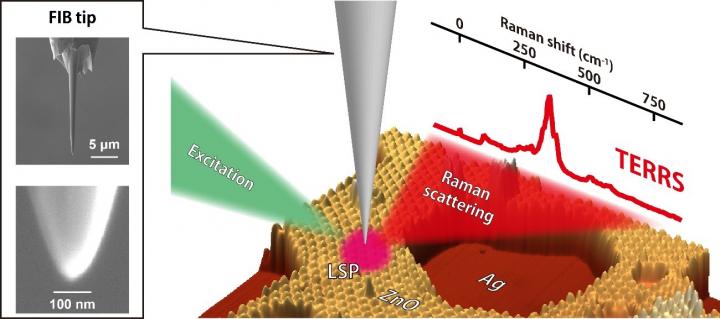
Tip-enhanced resonance Raman scattering is measured by a silver tip fabricated by focused ion beam (FIB) milling. Localized surface plasmon (LSP) is excited by an excitation laser, which generates enhanced Raman scattering from ultrathin zinc oxide (ZnO) films grown on a single-crystal silver (Ag) surface. Credit: Takashi Kumagai
A research team at Fritz-Haber Institute in Berlin, headed by Dr. Takashi Kumagai, demonstrated tip-enhanced “resonance” Raman spectroscopy.
Resonance Raman spectroscopy is a powerful tool to analyze a specific chemical structure at a high sensitivity, but its spatial resolution has been restricted to be a few hundred nm due to the diffraction limit.
Extreme field confinement at a metal tip apex through localized surface plasmon excitation allows to break this limitation and now attain 1-nm resolution.
Tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy takes advantage of atomic resolution imaging of scanning probe microscopy and enhanced Raman scattering through localized surface plasmon excitation.
The research team revealed tip-enhanced resonance Raman scattering in which both physical and chemical enhancement mechanisms are operative.
The underlying process was examined by modifying the localized surface plasmon resonance in the scanning tunneling microscope junction and by recording different-thickness zinc oxide films that exhibit a slightly different electronic structure.
In addition, the correlation between tip-enhanced resonance Raman scattering and local electronic states is resolved in combination with scanning tunneling spectroscopy that maps the local electronic state of the zinc oxide film.
The results explicitly show that a confined electromagnetic field can interact with local electronic resonances at the (sub)nanometer scale.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



