Stress-relief substrate helps OLED stretch two-dimensionally?
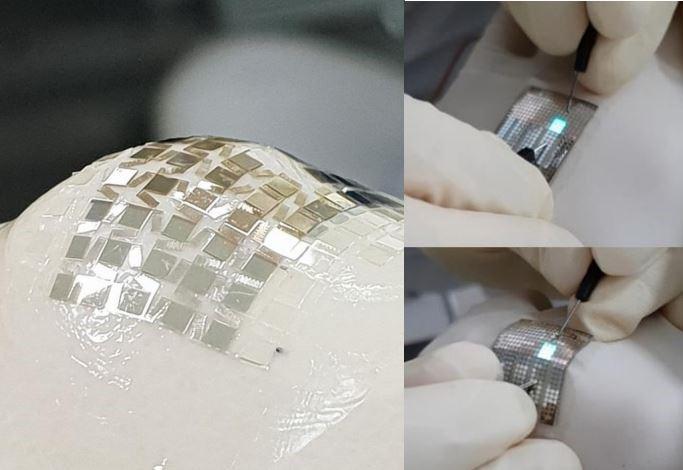
Photographs of the patterned rigid part of the substrate on the finger joint indicating 2D dimensional stretchability and images of stretchable OLEDs on a finger joint emitting green light. Credit: Professor Kyung Cheol Choi, KAIST Usage Restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
A KAIST team created stretchable OLEDs (Organic Light-Emitting Diodes) that are compliant and maintain their performance under high-strain deformation. Their stress-relief substrates have a unique structure and utilize pillar arrays to reduce the stress on the active areas of devices when strain is applied.
Traditional intrinsically stretchable OLEDs have commercial limitations due to their low efficiency in the electrical conductivity of the electrodes. In addition, previous geometrically stretchable OLEDs laminated to the elastic substrates with thin film devices lead to different pixel emissions of the devices from different peak sizes of the buckles.
To solve these problems, a research team led by Professor Kyung Cheol Choi designed a stretchable substrate system with surface relief island structures that relieve the stress at the locations of bridges in the devices. Their stretchable OLED devices contained an elastic substrate structure comprising bonded elastic pillars and bridges. A patterned upper substrate with bridges makes the rigid substrate stretchable, while the pillars decentralize the stress on the device.
Although various applications using micropillar arrays have been reported, it has not yet been reported how elastic pillar arrays can affect substrates by relieving the stress applied to those substrates upon stretching.
Compared to results using similar layouts with conventional free-standing, flat substrates or island structures, their results with elastic pillar arrays show relatively low stress levels at both the bridges and plates when stretching the devices.
They achieved stretchable RGB (red, green, blue) OLEDs and had no difficulties with material selection as practical processes were conducted with stress-relief substrates.
Their stretchable OLEDs were mechanically stable and have two-dimensional stretchability, which is superior to only one-direction stretchable electronics, opening the way for practical applications like wearable electronics and health monitoring systems.
Professor Choi said, “Our substrate design will impart flexibility into electronics technology development including semiconductor and circuit technologies. We look forward this new stretchable OLED lowering the barrier for entering the stretchable display market.”
###
This research was published in Nano Letters titled Two-Dimensionally Stretchable Organic Light-Emitting Diode with Elastic Pillar Arrays for Stress Relief. This work was supported by the Engineering Research Center of Excellence Program supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

Magnetic tornado is stirring up the haze at Jupiter’s poles
Unusual magnetically driven vortices may be generating Earth-size concentrations of hydrocarbon haze. While Jupiter’s Great Red Spot has been a constant feature of the planet for centuries, University of California,…

Cause of common cancer immunotherapy side effect s
New insights into how checkpoint inhibitors affect the immune system could improve cancer treatment. A multinational collaboration co-led by the Garvan Institute of Medical Research has uncovered a potential explanation…

New tool makes quick health, environmental monitoring possible
University of Wisconsin–Madison biochemists have developed a new, efficient method that may give first responders, environmental monitoring groups, or even you, the ability to quickly detect harmful and health-relevant substances…



