Tryptophan supports guts health on trouts under stress
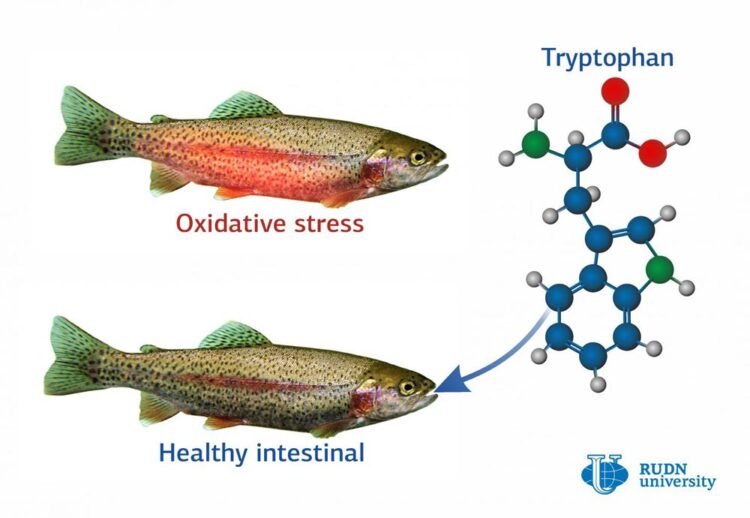
A biologist from RUDN University found the most beneficial concentration of tryptophan for rainbow trout. When added to the diet of the fish, this amino acid supports the immune system and reduces the oxidative stress in the intestinal tract caused by the overpopulation of fish farms.
Credit: RUDN
A biologist from RUDN University found the most beneficial concentration of tryptophan for rainbow trout. When added to the diet of the fish, this amino acid supports the immune system and reduces the oxidative stress in the intestinal tract caused by the overpopulation of fish farms. The results of the study were published in the Aquaculture magazine.
The fish in fish farms is under constant stress because of overpopulation, transportation, malnutrition, and low quality of water. All these factors have a negative impact on the health of the fish and cause diseases and death. However, they cannot be completely eliminated: it makes financial sense to keep a lot of fish in small farms, as it increases production volumes.
The consequences of overpopulation include weak immunity, changes in chemical processes in fish bodies, and oxidative stress (cell death as a result of oxidation). In particular, oxidative stress can cause intestinal tract walls to become thinner which makes fish more susceptible to dangerous pathogens. A biologist from RUDN University conducted an experiment and found a way to protect the fish from oxidative stress without putting additional financial burden on fish farms.
Tryptophan is an amino acid that affects the immune system and supports the antioxidant response, i.e. a body’s ability to resist oxidative stress. Tryptophan is used to treat depression in humans and is also added to animal foodstuff to make it more balanced. Its production is cheap, making it easily available in the market. The scientist from RUDN University studied the effect of tryptophan on enzyme activity and the expression of immune genes in the intestinal tracts of fish.
The subject of the study was Oncorhynchus mykiss or rainbow trout that is quite popular in fish farming. Two groups of trout were kept in an underpopulated (15 kg of fish per 1 square meter) and overpopulated (25 kg per 1 square meter) enclosure respectively. In each group, three subgroups were identified. Each subgroup got its own diet with either no tryptophan, 5 or 10 grams of tryptophan per 1 kg of feed. After 70 days the scientists assessed the level of oxidation stress resistance in the intestinal tracts of the fish by measuring enzyme activity and the expression of genes that participate in immune and antioxidant response.
The fish that consumed 5 g of tryptophan showed higher stress resistance levels than the fish that received no amino acid at all: enzymes and genes in charge of the antioxidant response were 1.5-2 times more active in the former group. However, a higher dosage of tryptophan (10 g) reduced gene expression and slowed down the activity of antioxidant enzymes.
“Adding 5 g of tryptophan per 1 kg of feed increased the immune response in the intestinal tract of rainbow trout and therefore reduced the oxidative stress even in the conditions of overpopulation. However, larger amounts of tryptophan weaken the reaction to stress factors which may be harmful for fish health”, said Prof. Morteza Yousefi, PhD from the Department of Veterinary Medicine, RUDN University.
The results of the study can help prevent the death of fish while preserving high density of fish population in farms. Prof. Yousefi plans to focus his future studies on more in-depth details.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

You are What You Eat—Stanford Study Links Fiber to Anti-Cancer Gene Modulation
The Fiber Gap: A Growing Concern in American Diets Fiber is well known to be an important part of a healthy diet, yet less than 10% of Americans eat the minimum recommended…

Trust Your Gut—RNA-Protein Discovery for Better Immunity
HIRI researchers uncover control mechanisms of polysaccharide utilization in Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Researchers at the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI) and the Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) in Würzburg have identified a…

ASXL1 Mutation: The Hidden Trigger Behind Blood Cancers and Inflammation
Scientists show how a mutated gene harms red and white blood cells. LA JOLLA, CA—Scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) have discovered how a mutated gene kicks off…



