Medical robotic hand? Rubbery semiconductor makes it possible
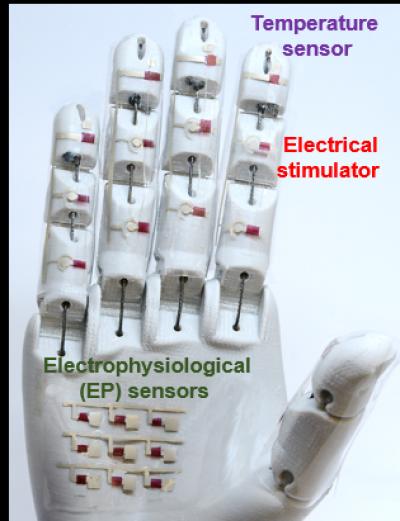
A medical robotic hand is just one potential application for the rubbery electronics reported by researchers.
Credit: University of Houston
Rubbery electronics offer promise for new applications
A medical robotic hand could allow doctors to more accurately diagnose and treat people from halfway around the world, but currently available technologies aren’t good enough to match the in-person experience.
Researchers report in Science Advances that they have designed and produced a smart electronic skin and a medical robotic hand capable of assessing vital diagnostic data by using a newly invented rubbery semiconductor with high carrier mobility.
Cunjiang Yu, Bill D. Cook Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering at the University of Houston and corresponding author for the work, said the rubbery semiconductor material also can be easily scaled for manufacturing, based upon assembly at the interface of air and water.
That interfacial assembly and the rubbery electronic devices described in the paper suggest a pathway toward soft, stretchy rubbery electronics and integrated systems that mimic the mechanical softness of biological tissues, suitable for a variety of emerging applications, said Yu, who also is a principal investigator at the Texas Center for Superconductivity at UH.
The smart skin and medical robotic hand are just two potential applications, created by the researchers to illustrate the discovery’s utility.
In addition to Yu, authors on the paper include Ying-Shi Guan, Anish Thukral, Kyoseung Sim, Xu Wang, Yongcao Zhang, Faheem Ershad, Zhoulyu Rao, Fengjiao Pan and Peng Wang, all of whom are affiliated with UH. Co-authors Jianliang Xiao and Shun Zhang are affiliated with the University of Colorado.
Traditional semiconductors are brittle, and using them in otherwise stretchable electronics has required special mechanical accommodations. Previous stretchable semiconductors have had drawbacks of their own, including low carrier mobility – the speed at which charge carriers can move through a material – and complicated fabrication requirements.
Yu and collaborators last year reported that adding minute amounts of metallic carbon nanotubes to the rubbery semiconductor of P3HT – polydimethylsiloxane composite – improves carrier mobility, which governs the performances of semiconductor transistors.
Yu said the new scalable manufacturing method for these high performance stretchable semiconducting nanofilms and the development of fully rubbery transistors represent a significant step forward.
The production is simple, he said. A commercially available semiconductor material is dissolved in a solution and dropped on water, where it spreads; the chemical solvent evaporates from the solution, resulting in improved semiconductor properties.
It is a new way to create the high quality composite films, he said, allowing for consistent production of fully rubbery semiconductors.
Electrical performance is retained even when the semiconductor is stretched by 50%, the researchers reported. Yu said the ability to stretch the rubbery electronics by 50% without degrading the performance is a notable advance. Human skin, he said, can be stretched only about 30% without tearing.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Medical Engineering
The development of medical equipment, products and technical procedures is characterized by high research and development costs in a variety of fields related to the study of human medicine.
innovations-report provides informative and stimulating reports and articles on topics ranging from imaging processes, cell and tissue techniques, optical techniques, implants, orthopedic aids, clinical and medical office equipment, dialysis systems and x-ray/radiation monitoring devices to endoscopy, ultrasound, surgical techniques, and dental materials.
Newest articles

Parallel Paths: Understanding Malaria Resistance in Chimpanzees and Humans
The closest relatives of humans adapt genetically to habitats and infections Survival of the Fittest: Genetic Adaptations Uncovered in Chimpanzees Görlitz, 10.01.2025. Chimpanzees have genetic adaptations that help them survive…

You are What You Eat—Stanford Study Links Fiber to Anti-Cancer Gene Modulation
The Fiber Gap: A Growing Concern in American Diets Fiber is well known to be an important part of a healthy diet, yet less than 10% of Americans eat the minimum recommended…

Trust Your Gut—RNA-Protein Discovery for Better Immunity
HIRI researchers uncover control mechanisms of polysaccharide utilization in Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Researchers at the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI) and the Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) in Würzburg have identified a…



