Specific and rapid expansion of blood vessels
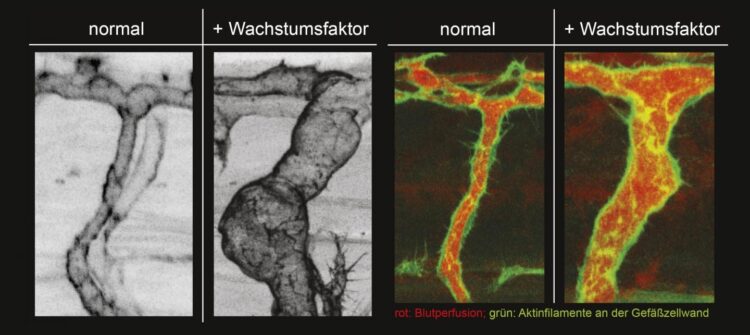
(A,B) in vivo image of growing artery (yellow arrowhead) in control scenario (A) and upon growth factor stimulation (B). (C,D) Confocal image of arterial blood flow (red) and arterial endothelial actin cytoskeleton (green) in control scenario (C) and upon growth factor stimulation (D).
Credit: ZOO, KIT
Nature Communications: KIT researchers identify a new mechanism to control endothelial cell size and arterial caliber – basis for better treatment of heart infarct and stroke.
Upon a heart infarct or stroke, rapid restoration of blood flow, and oxygen delivery to the hypo perfused regions is of eminent importance to prevent further damage to heart or brain. Arterial diameter is a critical determinant of blood flow conductance. Scientists of the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) have now discovered a novel mechanism to structurally increase arterial diameter by selectively increasing the size of arterial endothelial cells, thereby allowing rapid increases in flow. The team has published their results in Nature Communications (DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19008-0).
Research team leader Professor Ferdinand le Noble of the Department of Cell and Developmental Biology at the KIT explains that the prevalence of complex vascular disease is steadily rising and it is especially this patient population that will benefit from adjunct therapy to conventional revascularization methods. Unfortunately, many recent clinical therapeutic vascular growth trials failed, thus emphasizing the need for a more rational approach to this important area of clinical cardiovascular medicine, le Noble explains.
His research team now identified a novel mechanism to improve arteriogenesis involving enlargement of the endothelial cells lining the arteries. Larger endothelial cells allow a structural increase of arterial diameter in developing vascular networks. “This is important, as already small increases in arterial diameter considerably augment flow conductance, a simple physical principle,” le Noble explains.
The process of cell enlargement is coordinated by a molecule called Trio. Trio is located inside the endothelial cell and plays a pivotal role in determining endothelial shape. Trio does this by selectively activating specific molecules, so called small Rho GTPases, that affect the structure and rigidity of the endothelial cytoskeleton in the cell periphery. The authors show that Trio can be activated selectively in developing arteries by precisely titrating Vegf signaling strength in the arterial wall. This is achieved by targeting soluble Vegf receptor Flt1, a decoy receptor for the growth factor VEGF. Endothelial cell enlargement is a fast process, independent of shear stress or inflammatory processes and within several hours results in 2-3 fold structurally larger arterioles that can attract flow to hypoperfused regions. Due to the rapid nature of this process, the authors believe that this approach has significant advantages over the (relatively slow) conventional angiogenesis approaches aimed at improving vessel number.
“We hope that our research can contribute to improving the treatment of ischemic cardiovascular diseases” le Noble says. “Our data derived from experimental models and human endothelial cells suggest that Trio is an interesting therapeutic target, and together with our collaboration partners, we envision to extend our work to pre-clinical models.”
###
The study was financed by the German Research Foundation (DFG) and carried out by KIT in cooperation with the German Center for Cardiovascular Research (DZHK) at its partner sites in Heidelberg, Göttingen, and Munich, the WWU Münster, and colleagues from the Netherlands (Sanquin, Amsterdam) and Finland (Wihuri research institute, Helsinki).
Original publication:
Klems, A., van Rijssel, J., Ramms, Anne S., Wild, R., Hammer, J., Merkel, M., Derenbach, L. Préau, L., Hinkel, R., Suarez-Martinez, I., Schulte-Merker, S., Vidal, R., Sauer, S., Kivelä, R., Alitalo, K., Kupatt, C., van Buul, J. D., le Noble, F. (2020): The GEF Trio controls endothelial cell size and arterial remodeling downstream of Vegf signaling in both zebrafish and cell models. Nature Communications, 2020, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19008-0
Publication in Nature Communications: https:/
Press Contact: Margarete Lehné, Deputy Head of Press Office,
Phone: +49 721 608-41157, margarete.lehne@kit.edu
Being “The Research University in the Helmholtz Association”, KIT creates and imparts knowledge for the society and the environment. It is the objective to make significant contributions to the global challenges in the fields of energy, mobility, and information. For this, about 9,300 employees cooperate in a broad range of disciplines in natural sciences, engineering sciences, economics, and the humanities and social sciences. KIT prepares its 24,400 students for responsible tasks in society, industry, and science by offering research-based study programs. Innovation efforts at KIT build a bridge between important scientific findings and their application for the benefit of society, economic prosperity, and the preservation of our natural basis of life. KIT is one of the German universities of excellence.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



