A new model found to predict earthquake propagation speed
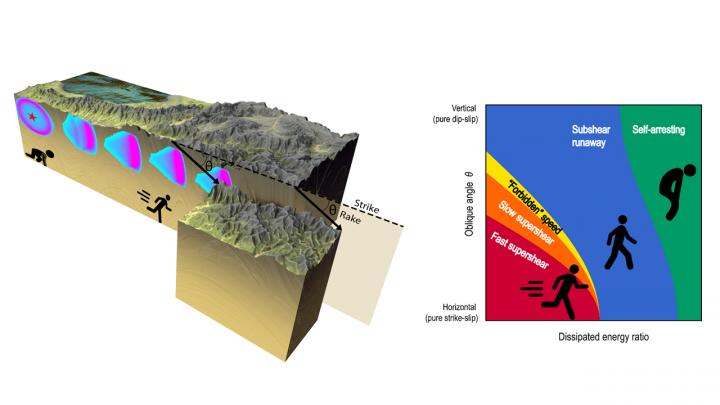
Left : an earthquake rupture with oblique slip. The surface cutting through the Earth's crust is a fault. The oblique offset of the small block indicates the direction of slip. The colors on the fault plane show the amount of fault slip at five successive times, generated by a computer simulation. The slip is limited in depth and sweeps along the fault at a speed called the rupture speed.
Right : the rupture speeds that large oblique-slip earthquakes can achieve.
This diagram shows how the steady rupture speeds of large earthquakes in the new model by Weng and Ampuero (2020) depend on the slip-obliqueness angle and on the strength of the fault.
Credit: H. Weng and J.P. Ampuero, Nature Geoscience (2020).
Among the most damaging natural hazards, earthquakes are still today one of the least understood phenomena in Earth Sciences. Earthquakes happen when rocks on either side of a tectonic fault slide. The sliding, however, does not occur along the whole fault at once but starts at one point, the hypocenter, and then spreads over the entire fault at a speed known as the “rupture speed” of the earthquake. Geophysicists are particularly interested in rupture speeds because the faster they are, the stronger the seismic waves and therefore the greater the damage caused.
Seismic models developed so far concluded that earthquakes could not propagate in a stable and sustainable way at arbitrary speeds. Scientists had therefore determined a “forbidden speed” range situated between the speed of P and S waves, the two main seismic waves that propagate through the Earth. However, progress in the seismological observation of earthquakes has made it possible to demonstrate that recent earthquakes had actually propagated within the forbidden range. Such was the case for the 2018 earthquake in Palu, Indonesia, for example, which caused a destructive tsunami.
Uninterrupted rupture speeds due to oblique sliding
To resolve this puzzling inconsistency between earthquake theory and observations, researchers of Université Côte d’Azur and the IRD developed a new model to predict the propagation speed of earthquakes. This feat was accomplished using the high-performance computer of the Côte d’Azur Observatory, one of the participants in OPAL, a shared platform that provides access to all the computational resources of the region.
The researchers managed to overcome two crucial limitations of the previous models. The first was to rely on 2-dimensional models, while the Earth is 3-dimensional. The second was to assume either a horizontal or a vertical direction of sliding, while earthquake sliding can be oblique. By overcoming these two limitations, they were able to explain why the “forbidden speeds” are actually admissible.
“One of the main challenges in the prevention of earthquakes is to predict their impact. We need to seize this opportunity to introduce more physics in the evaluation of seismic hazards, which has been very empirical so far,” points out Huihui Weng, researcher at Université Côte d’Azur. “The new model provides validated theoretical elements which could ultimately be used to improve the way seismic risk is evaluated,” adds Jean-Paul Ampuero, seismologist at the IRD.
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



